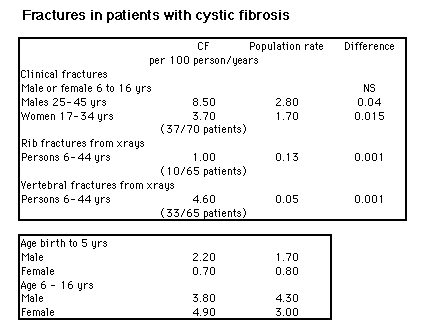
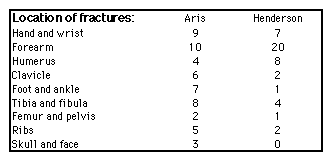
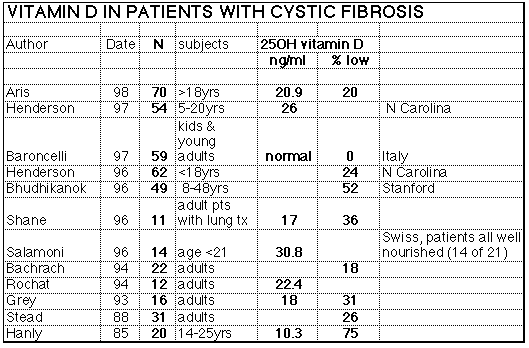
These are some illustrations from a talk given to our cystic fibrosis group on April 24, 1998. The presentation will need some revising for the Web, but here it is for now:
This is a review of published literature that reports spinal bone density in either T or Z scores. In young adults the T scores are the same as Z scores so I substituted them.
| Number | Subjects | Z-score |
|---|---|---|
| 11 | Adult lung tx | -2.50 |
| 20 | adult lung tx | -2.14 |
| 16 | adults | -1.40 |
| 10 | adults | -1.47 |
| 70 | adults | -2.40 |
| 22 | adults | -2.80 |
| 49 | adults and children | -1.74 |
| 31 | adults and children | -1.00 |
| 62 | children | -1.30 |
| 28 | girls QCT | -0.31 |
| 29 | boys QCT | -0.97 |



FACTORS THAT COULD LEAD TO BONE DISEASE in patients with cystic fibrosis Malabsorption of vitamin D of calcium (.118 in normals .090 CF without enzymes .110 CF with enzymes) of general nutrients Low Vitamin D levels also depends on sun exposure measure 25 OH instead of 1,25(OH)2 unless: renal failure ketoconazole (can reduce 1,25) unexplained calcium abnormalities Hypogonadism high incidence in adult patients usually hypogonadotrophic Inactivity Respiratory acidosis Cytokines from chronic infections
TREATMENT OF BONE DISEASE in patients with cystic fibrosis Malabsorption Nutritional support Especially calcium Try calcium citrate Low Vitamin D levels Replace with 800-1000 units/day or more follow 25 OH vitamin D levels Hypogonadism Give teens and women estrogen if needed Avoid depo-provera Give males testosterone Inactivity Encourage exercise Respiratory acidosis - treat Cytokines from chronic infections - treat Use corticosteroids only when necessary In some cases may use calcitonin to mitigate effects But there MUST be adequate calcium/vitamin D Consider growth hormone
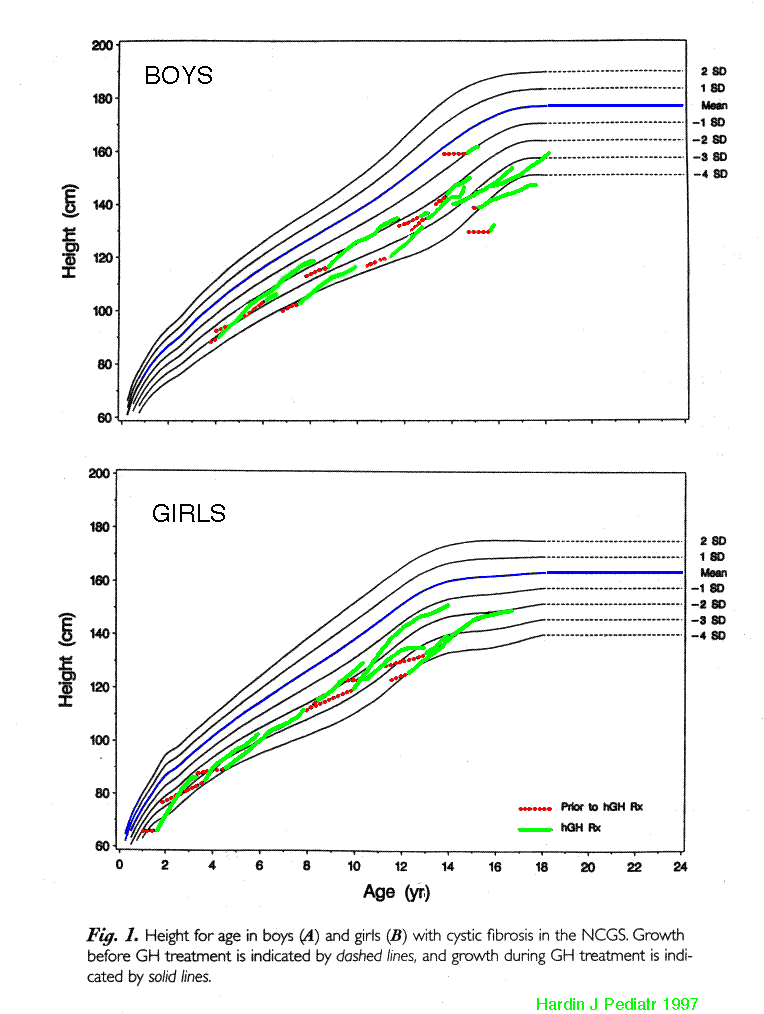
WHY TO AVOID BISPHOSPHONATES in patients with cystic fibrosis Etidronate (Didronel) Pamidronate (Aredia) Alendronate (Fosamax) May cause osteomalacia Patients with C.F. already prone to this May inhibit primary modeling of growing bone Safety in children not established only reported in a few cases should do bone biopsies if done on research basis Half-life in bone is >10 years! Poor absorption in normals probably worse in C.F.
2. Aris RM, Renner JB, Winders AD, Buell HE, Riggs DBL, Ontjes DA. Increased rate of fractures and severe kyphosis: sequelae of living into adulthood with cystic fibrosis. Ann Intern Med. 1998; 128: 186-93.
3. Bachrach LK, Loutit CW, Moss RB. Osteopenia in adults with cystic fibrosis. Am J Med. 1994; 96: 27-34.
4. Baroncelli GI, De Luca F, Magazz'u G, Arrigo TSC, Catena C, Bertelloni S, et al. Bone demineralization in cystic fibrosis: evidence of imbalance between bone formation and degradation. Pediatr Res. 1997; 41: 397-403.
5. Bhudhikanok GS, Lim J, Marcus R, Harkins A, Moss RBB. Correlates of osteopenia in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics. 1996; 97: 103-11.
6. De Schepper J, Smitz J, Dab I, Piepsz A, Jonckheer MBP. Low serum bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein concentrations in patients with cystic fibrosis: correlation with hormonal parameters and bone mineral density. Horm Res. 1993; 39: 197-201.
7. Grey AB, Ames RW, Matthews RD, Reid IR. Bone mineral density and body composition in adult patients with cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 1993; 48: 589-93.
8. Hardin DS, Sy JP. Effects of growth hormone treatment in children with cystic fibrosis: the National Cooperative Growth Study experience. J Pediatr. 1997; 131: S65-9.
9. Henderson RC, Lester G. Vitamin D levels in children with cystic fibrosis. South Med J. 1997; 90: 378-83.
10. Henderson RC, Madsen CD. Bone density in children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1996; 128: 28-34.
11. Henderson RC, Specter BB. Kyphosis and fractures in children and young adults with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1994; 125: 208-12.
12. Huseman CA, Colombo JL, Brooks MA, Smay JRG, Sammut PH, Bier DM. Anabolic effect of biosynthetic growth hormone in cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1996; 22: 90-5.
13. Lipnick RN, Glass RB. Bone changes associated with cystic fibrosis. Skeletal Radiol. 1992; 21: 115-6.
14. Peters SA, Rolles CJ. Vitamin therapy in cystic fibrosis--a review and rationale. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1993; 18: 33-8.
15. Rochat T, Slosman DO, Pichard C, Belli DC. Body composition analysis by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in adults with cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1994; 106: 800-5.
16. Salamoni F, Roulet M, Gudinchet F, Pilet M, Thi'ebaud DBP. Bone mineral content in cystic fibrosis patients: correlation with fat-free mass. Arch Dis Child. 1996; 74: 314-8.
17. Shane E, Silverberg SJ, Donovan D, Papadopoulos ASR, Addesso V, Jorgesen B, et al. Osteoporosis in lung transplantation candidates with end-stage pulmonary disease. Am J Med. 1996; 101: 262-9.
18. Stead. Vitamin D and parathryoid hormone and bone mineralisation in adults with cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 1988; 43: 190-194.
19. Stillwell PC, Mallory GBJ. Pediatric lung transplantation. Clin Chest Med. 1997; 18: 405-14.
20. Teramoto S, Matsuse T, Ouchi Y. Osteoporosis in lung transplantation candidates with end-stage pulmonary disease. Am J Med. 1997; 103: 334-6.