Cat Salivary Glands |
|
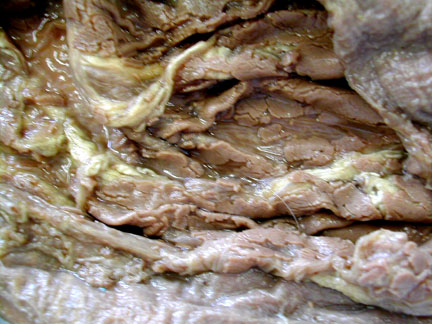
Submandibular gland is the exposed triangular shape in the lower left & the parotid gland is at the right.
|
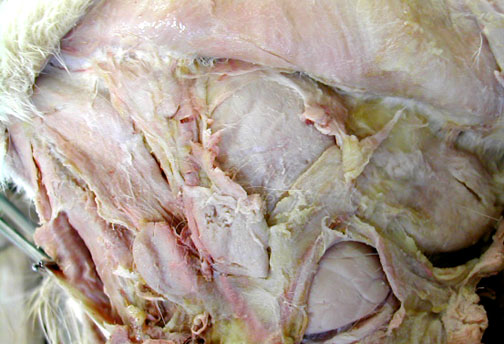
The massester muscle of the jaw is at the lower left, the submandibular gland is the oval at the lower right & above is part of the large, whitish parotid gland.
|
Cat "Mesenteries" |
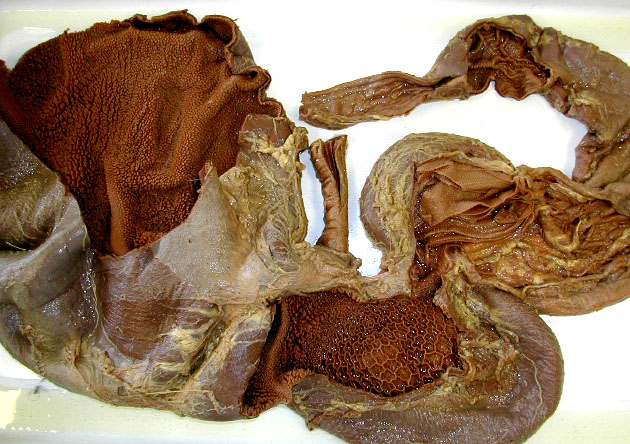
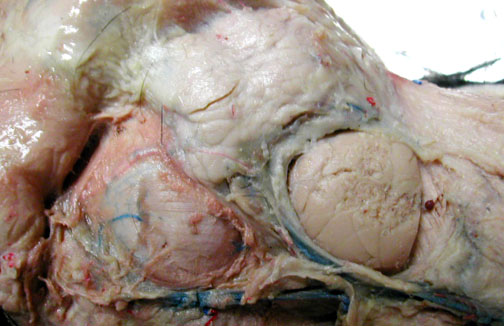
The greater omentum is a double wall of peritoneal membrane & may act as a fat storage organ.

|
Cat liver & greater omentum. Find the gall bladder in a pocket of liver tissue.
|
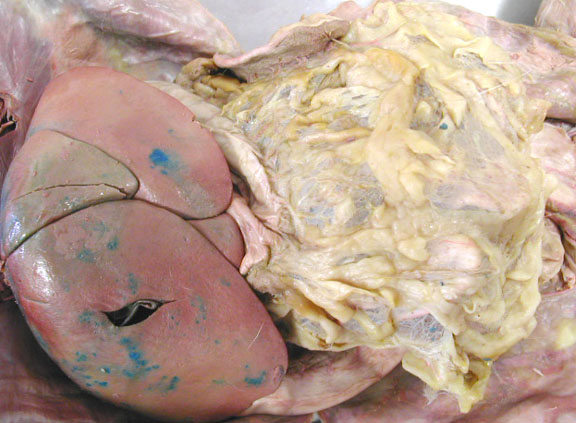
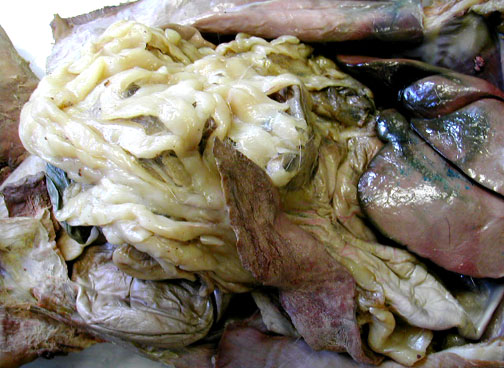
Another view of the greater omentum & the spleen which is really a cardiovascular organ.
|
The falciform ligament is a remnant of the umbilical cord & attaches between the major right & left lobes of the liver. The falciform then attaches to the diaphragm (cut here). Heart & lungs are also visible.
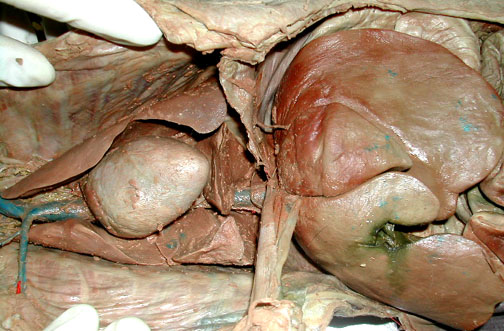
|
Cat: Abdominal Viscera |
|
View of the liver & intestines after removal of greater omentum. Find the gall bladder between folds of the liver in the lower left.
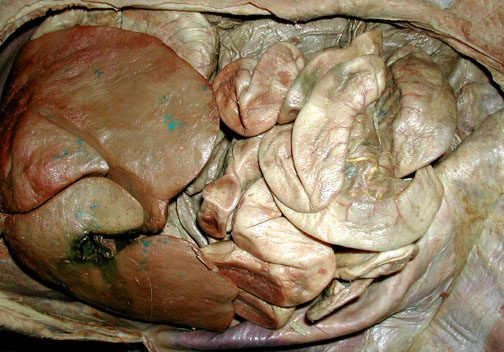
|
Leakage from the small, dark green gall bladder, stains surrounding portions of the liver green too.
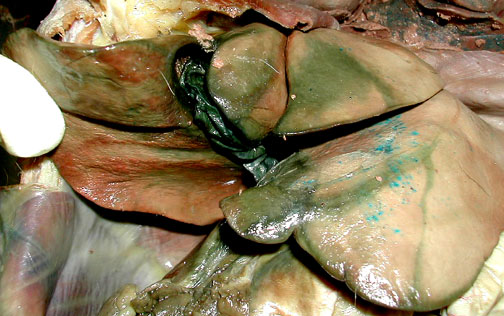
|
|
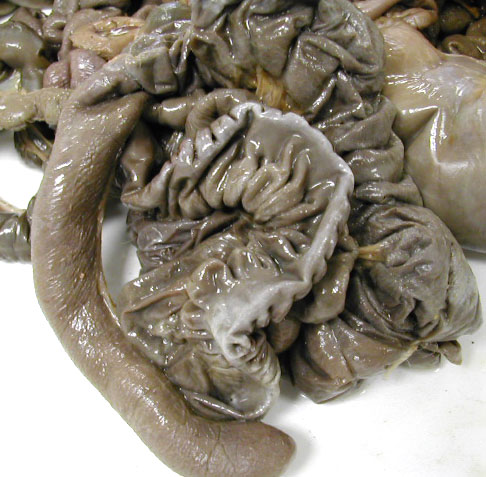
The cat cecum ends in the small side-pocket at the lower left, the colon extends upward & to the right.
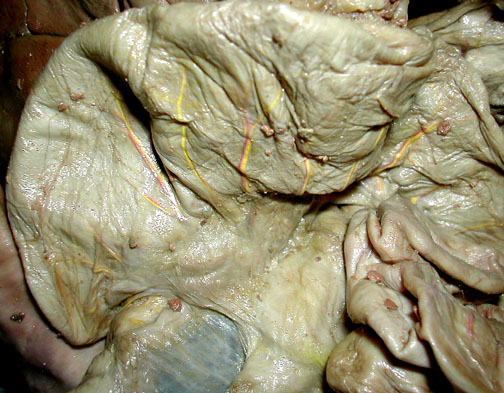
|
Pancreatic tissue in a cat extends in two thin sections, one section is beside the small intestine (stained, in part, in this view with some yellow latex) & the other passes underneath the greater omentum towards the right.
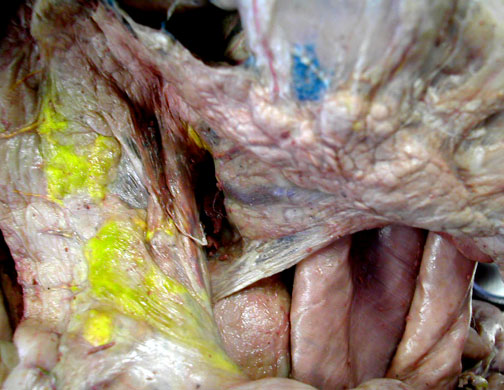
|
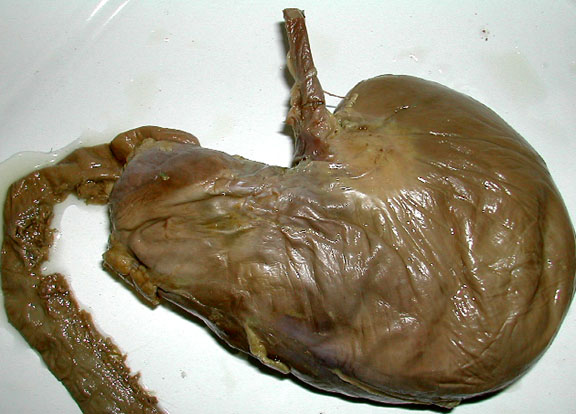
Stomach Exterior
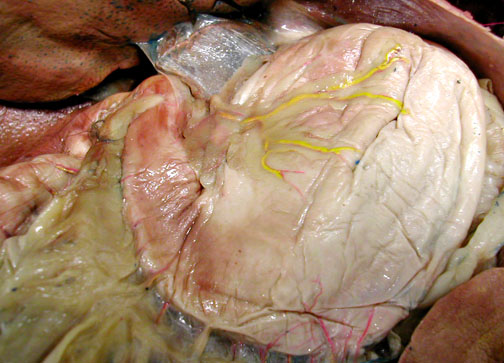
|
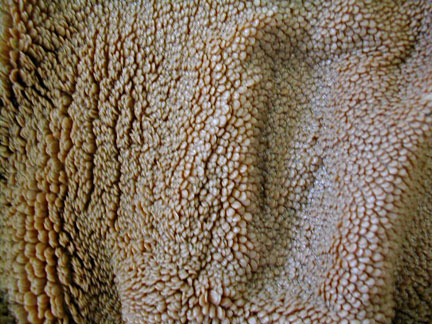
Stomach Rugae
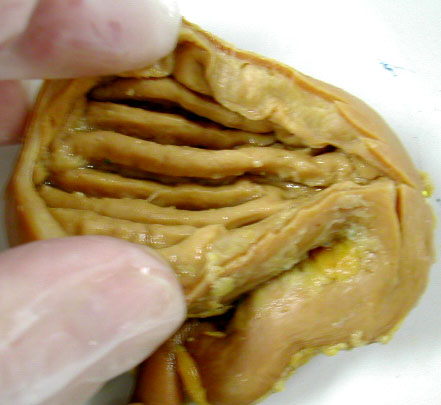
|
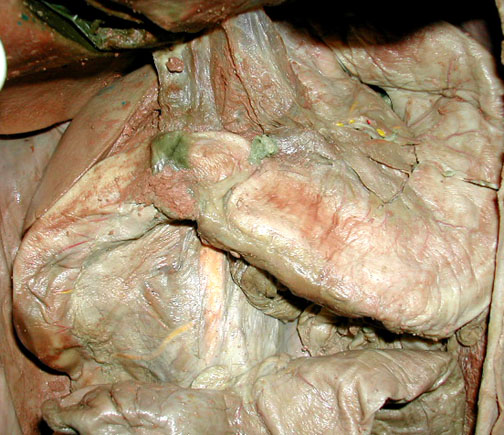
Pyloric region of Stomach - with duodenum
|
Duodenum (first section of small intestine) with part of pancreas.

|
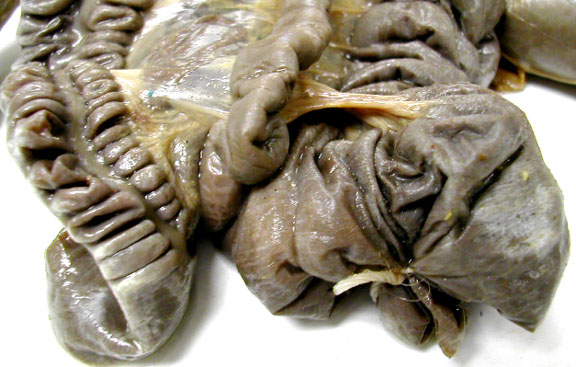
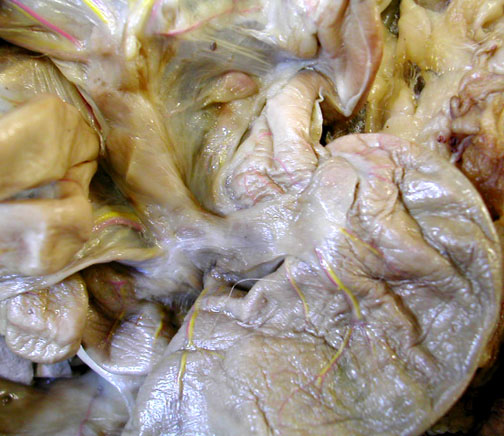
Ileocolic Junction has a sphincter controlling movement of materials from the small intestine into the colon.
|
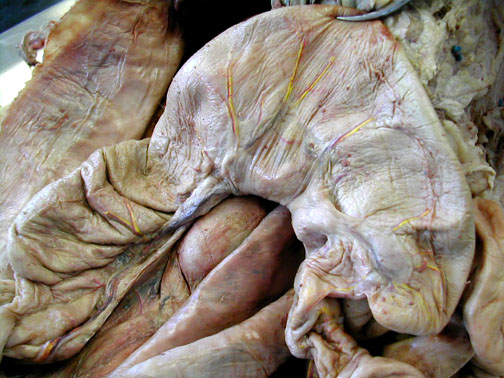
The cat's cecum is at the right & the colon extends in off to the left. The cecum of a cat is very small compared to that of a rabbit below.
|