Project No. 1:
Map Locations of Roads
& Cost Estimations
Submitted to:
Prof. Schiess
FE 345
Submitted by:
GROUP 3
Adam Hedin
Morgan E. Holen
Justin Knobel
Liz Stevens
10 April 2000
CONTENTS
I. Summary & Discussion
II. Map
III. GIS Map
IV. Cross Sections & Calculations
V. Road Cost Estimations Table
Summary & Discussion
The goal for the map
locations of roads project was to connect road 2070 to road 2000 without
leaving the Pack Forest property boundary.
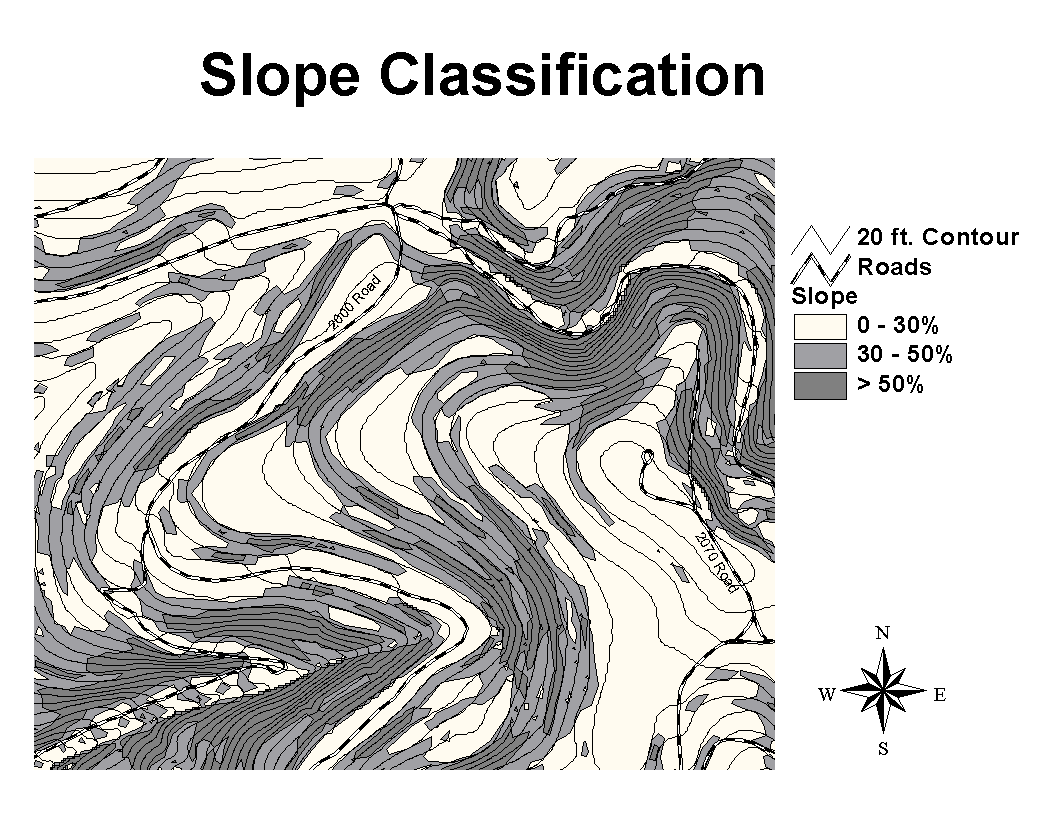
To begin, we created a slope class map to aid in the determination of the most feasible,
cost-effective route for each road alternative. Using a topographic map of Pack
Forest with 20’ contour lines, slope classes were measured with a set of
dividers and then drawn on a mylar overlay for
0-30%, 30-50% and >50% grade slope classes. Two roads were then pegged on a second mylar
overlay with a standard 15% maximum grade between each contour line, allowing
for a minimum curve radius of 60’ where applicable and < 35% sideslopes for
switchbacks. See Map.
Road 1 starts south of the
landing on the 2070 road and runs N64°W with a 15% grade for
approximately 400 feet then turns N84°W for approximately 133
feet. Road 1 continues going N64°W for another 661 feet then runs N30°W for 133 feet crossing the trail. The road continues going N80°W for another 667 feet at which point there
is a switchback. The road then goes for
approximately 380 feet at a bearing of N39°E until it reaches road
2000.
Road 2 begins on the landing at the trailhead and runs approximately 160 feet along the trail at N80°W and then parallels the trail at N61°W for approximately 680 feet at a 15% grade. The road then goes N80°W for 280 feet, then curves S38°W at a 15% grade for 100 feet. Continuing at an 11.25% grade, the road travels S18°E for 280 feet, then S11°E for 240 feet. For the next 280 feet, the road travels S21°E along a 7.5% grade, until it reaches a flat area (0% grade) and travels S68°W for 400 feet. Next is a switchback, then the road travels another 120 feet at a 15% grade going N35°W. In the final stretch, Road 2 curves around, going N61°E for 100 feet, then N31°W for 120, and N50°W for 120 feet all at a 15% grade until it meets road 2000.
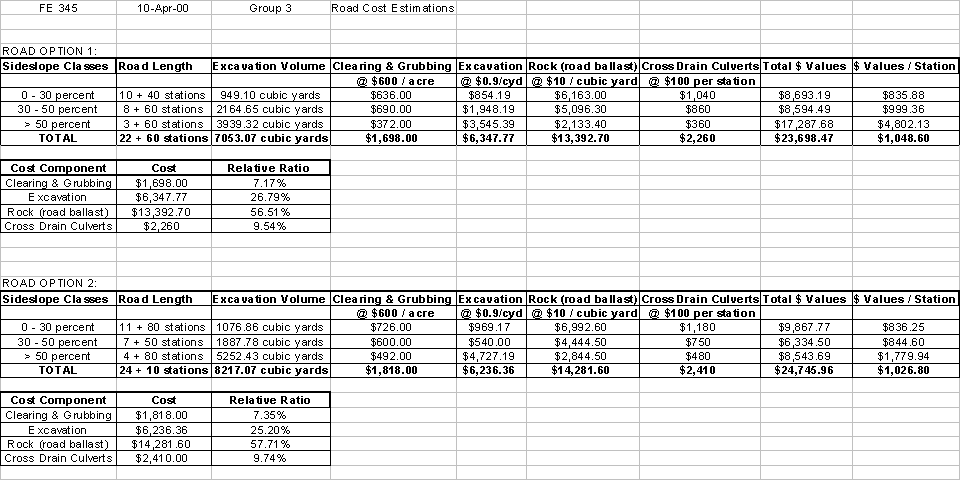
By
first calculating excavation volume, we discovered that Road 1 would require
7053.07 cubic yards to be moved and 8217.07 cubic yards for Road 2 (see Road
Cost Estimations Table). By then
calculating road costs, we found that constructing Road 1 would cost $1047.49
less than it would to build Road 2.
Road 2 is only 150 feet shorter than Road 1. The length of road in each slope class is proportionately
similar for both roads. For the
sideslope class 0-30%, it costs only $0.37 more per station to build Road 2. For the sideslope class 30-50%, it costs
$154.76 more per station, a considerable amount. For the sideslope class >50%, it costs $3022.19 more per
station, a substantial difference. All
in all, ballasts cost the most at $13,392.70 for Road 1 and $14,281.60 for Road
2.
Economically,
Road 1 is the better option as it is the less expensive of the two roads. However, Road 2 is cheaper per station by
about $22.00 and, although feet longer, it may be more economical as its design
is more conservative on paper. Road 1
may end up being longer in the field, and thus more expensive.
Environmentally, the shorter, less
steep road is typically preferable. In
our case, this is probably true, since a greater percentage of Road 2 – the
longer road – is in the >50% slope class.
This is potentially problematic, as steeper slopes increase the
probability of mass wasting and erosion.
This could be an economical consideration as well, because mass wasting
and erosion would require more maintenance and higher costs.
Road
2 may be safer to travel, since its overall grade is slightly less than that of
a Road 1. In the event of brake failure
or loss of traction, the shorter straight-aways on Road 2 would result in a
lower speed incident.
In conclusion, we chose Road
2. Although slightly longer, its design
is more feasible. It was designed more
conservatively, easing off of the 15% grade in critical areas. Since the financial difference between the
roads is so small, we feel that building the more conservative road would
result in little to no additional cost.

20%
Slope Cross Section
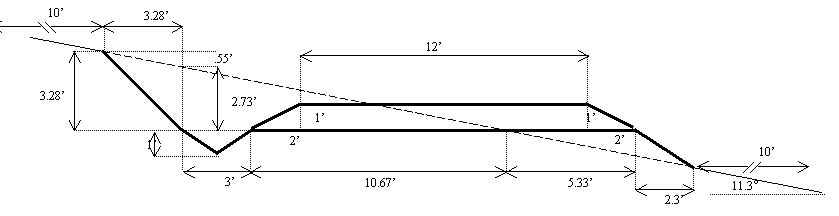
Cross
sectional excavation area:
![]()
Volume
for Road 1:
![]()
Volume
for Road 2:
![]()
![]()
Volume
for Road 1:
![]()
Volume
for Road 2:
![]()
Cross
sectional width:
![]()
Area
for Road 1:
![]()
Area
for Road 2:
![]()
40%
Slope Cross Section
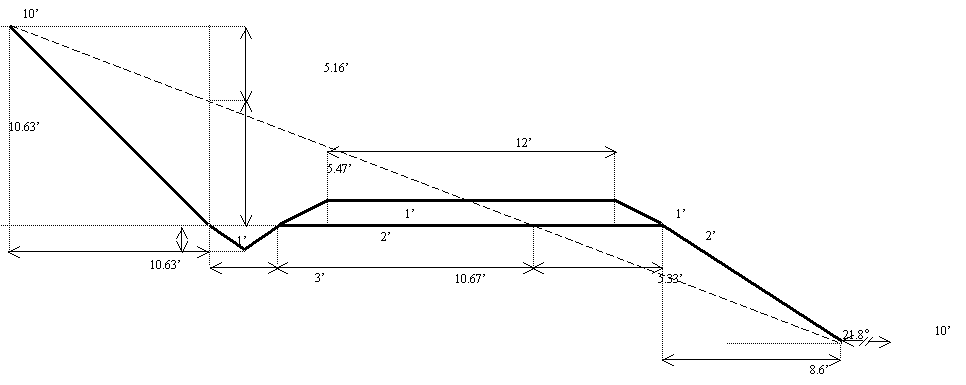
Cross
sectional excavation area:
![]()
Volume
for Road 1:
![]()
Volume
for Road 2:
![]()
![]()
Volume
for Road 1:
![]()
Volume
for Road 2:
![]()
Cross
sectional width:
![]()
Area
for Road 1:
![]()
Area
for Road 2:
![]()
60%
Slope Cross Section
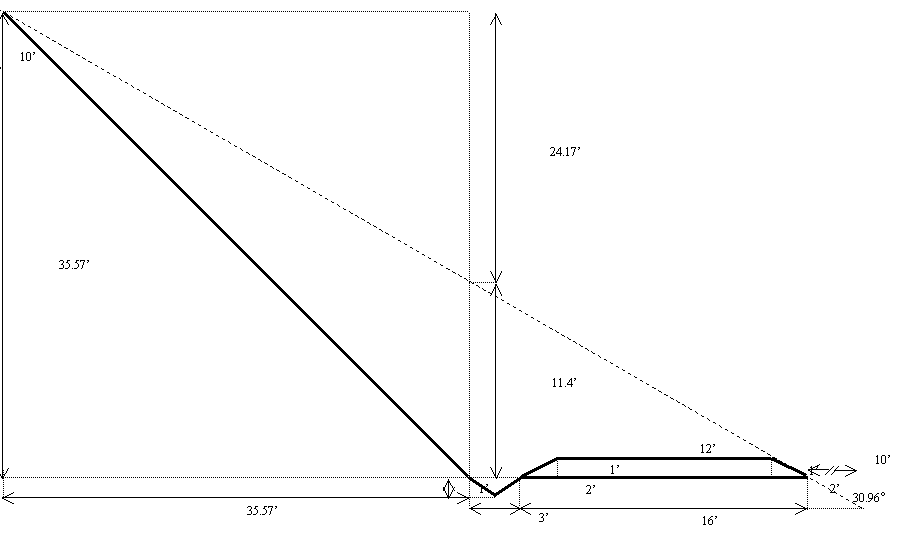
Cross
sectional excavation area:
![]()
Volume
for Road 1:
![]()
Volume
for Road 2:
![]()
![]()
Volume
for Road 1:
![]()
Volume
for Road 2:
![]()
Cross
sectional width:
![]()
Area
for Road 1:
![]()
Area
for Road 2:
![]()