
Pulmonary Function Testing
Case 8 Answers
A 64 year-old woman presents with complaints of dyspnea and orthopnea. She is a life-long non-smoker.
Her pulmonary function testing is as follows:
| Pre-Bronchodilator (BD) | Post- BD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | Actual | Predicted | % Predicted | Actual | % Change |
| FVC (L) | 1.00 | 2.51 | 40 | 1.02 | 3 |
| FEV1 (L) | 0.61 | 2.00 | 30 | 0.69 | 13 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 61 | 80 | 67 | 10 | |
| RV (L) | 1.15 | 1.55 | 74 | ||
| TLC (L) | 2.08 | 4.04 | 52 | ||
| RV/TLC (%) | 55 | 39 | |||
| Check abbreviations>> | |||||
Her spirometry is repeated with her in the upright and supine positions:
| Test | Upright | Supine |
|---|---|---|
| FVC (L) | 0.49 | 0.37 |
| FEV1 (L) | 0.82 | 0.68 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 0.60 | 0.54 |
| Check abbreviations>> |
Her flow volume loop is as follows:
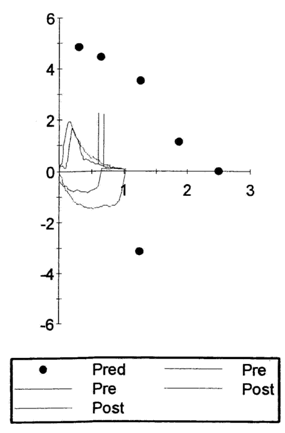
Case 8 Interpretation
This patient has a reduced FEV1 and FVC with a reduced FEV1/FVC ratio. She would, therefore, be classified as having an obstructive defect. However, she also has a low TLC (52% predicted). This is evidence of a restrictive defect and, therefore, this patient would be labeled as having a combined obstructive-restrictive defect. A DLCO is not provided which makes it difficult to determine if the cause of her restriction is due to a pulmonary parenchymal process or an extra-pulmonary process.
An important clue comes from her history. The patient reports orthopnea. Although this is classically seen in patients with heart failure, it is not specific for this disease. Patients with diaphragmatic weakness can also present with this symptom. When they lie supine, gravity no longer exerts an effect on the diaphragm and abdominal contents and the patients have trouble getting their diaphragm to descend against the abdominal contents on inspiration. The presence of diaphragmatic weakness is confirmed by repeating her pulmonary function tests with her in the upright and supine positions. When she is supine, her FVC and FEV1 both fall by greater than 20%, thus providing evidence that she may, in fact, have diaphragmatic weakness as the cause of her lung restriction.
UW School of Medicine : School of Medicine Mission
Copyright and Disclaimer : Credits and Acknowledgements