
Pleural Effusions
Case 10
A 55 year-old man presents with increasing dyspnea and is found to have a very large right pleural effusion occupying half of his chest cavity on chest x-ray. A thoracentesis is performed and 2.5 liters of serosanguinous fluid is removed. He initially feels like his breathing is markedly improved and the x-ray shows that you drained out most of the fluid in the pleural space. While you are awaiting the results of the pleural fluid studies, however, the patient develops increasing dyspnea at rest and his oxygen saturation falls to 85% on room air. You obtain a chest x-ray, which shows the following:
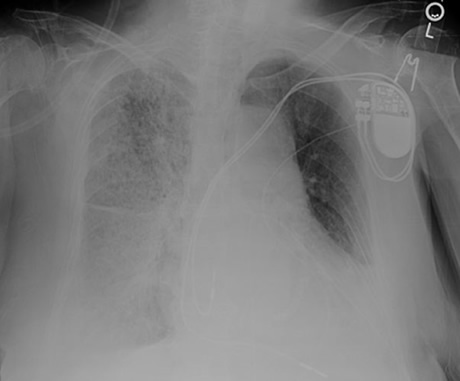
How would you interpret the chest x-ray on this patient?
What is the etiology of this increasing dyspnea and hypoxemia?
How could this have been prevented?
What is the appropriate management at this time?
UW School of Medicine : School of Medicine Mission
Copyright and Disclaimer : Credits and Acknowledgements