Introduction to Geographic Information
Systems in Forest Resources |
Exercise: Map Layouts
Objectives:
- Create a map using the ArcMap Layout interface
- Add various elements to the map layout
- Perform drive
substitution to create drives L (CD) and M (removable drive).
- Open a new map document
- Create a data frame and add some data
- Create a summary table from a attribute table
- Create a graph
- Create a layout & alter properties
- Add elements to the layout
Graph
Text
Graphic
Scale bar
Legend
North Arrow
- Save the layout as a template
- Print the layout
- Get more practice
- Poster example
Perform drive substitution
Perform drive
substitution to create the virtual drives L and M.
Open a new map document
- Create a directory (M:\maps).
- Enable the Spatial Analyst extension and view the Spatial Analyst toolbar.
- Start ArcMap and save the document as M:\maps\maps.mxd.
- Save frequently while making map layouts.
Create a data frame and add some data
- Create a new data frame and add L:\packgis\forest\roads, streams,
stands, and dem.
- Create a hillshade grid from, and then remove the dem grid. (Use Spatial Analyst > Surface Analysis > Hillshade.)
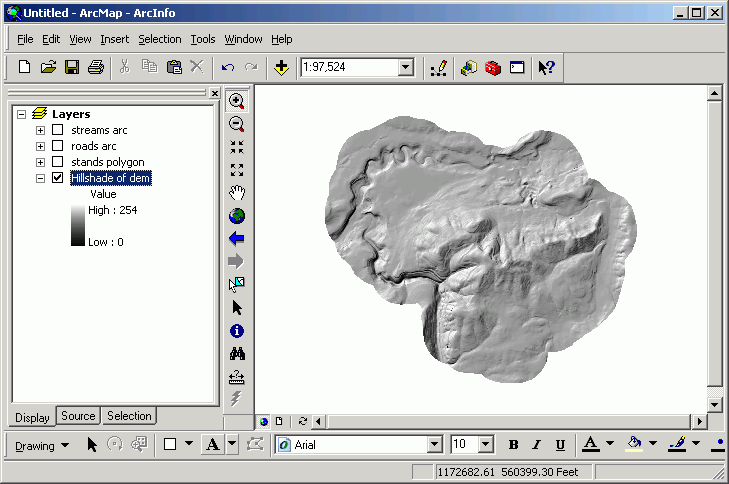
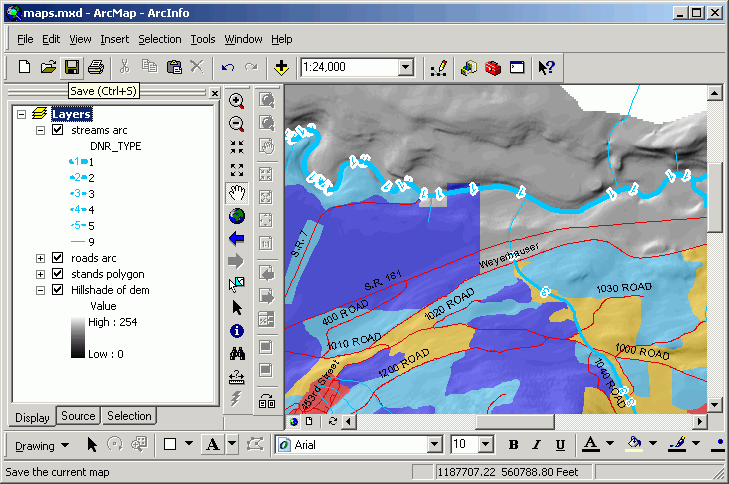
- Alter the polygon symbology for the stands layer.
- Use graduated colors based on the SITE_CLASS field.
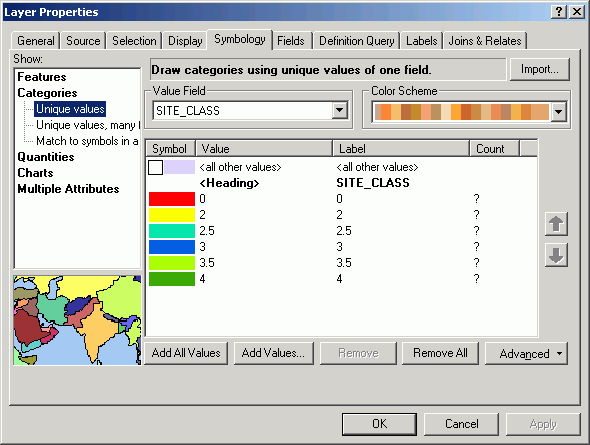
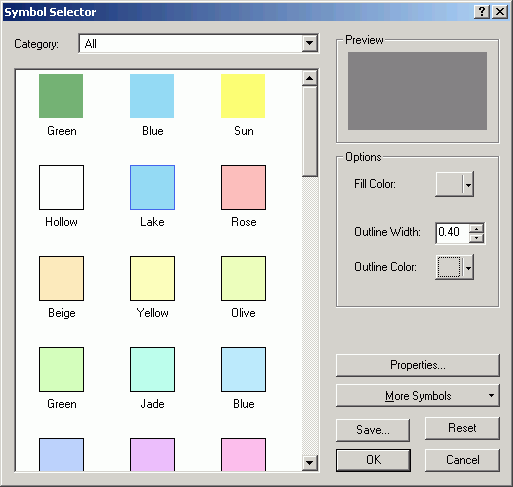
- Click Symbol and select Properties for All Symbols.
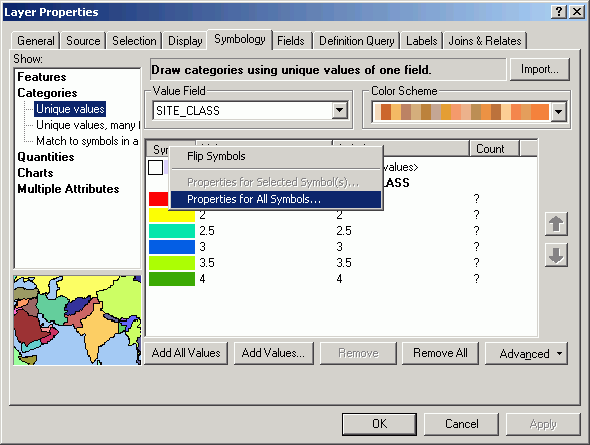
- Change the Outline Color to No Color.
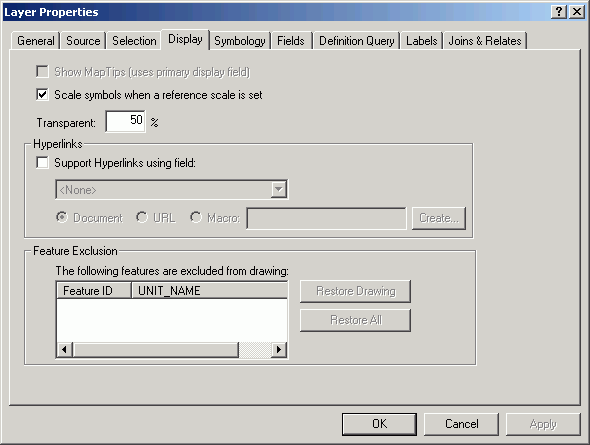
- Change the Display property and set the layer's transparency
to 50%. This will allow the hillshading to show through the stands.
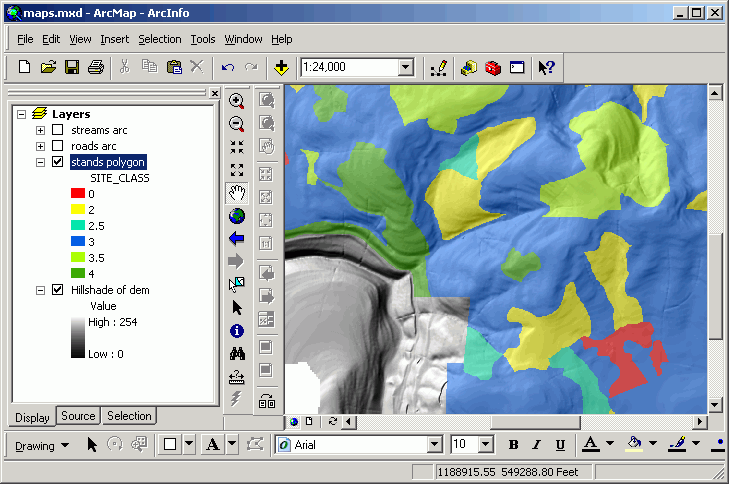
- Now the stands with the lower site class are red and yellow, moderates
are blue, and the highest values are green.
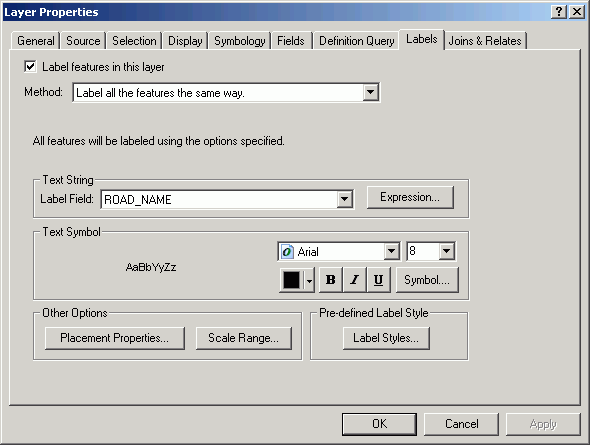
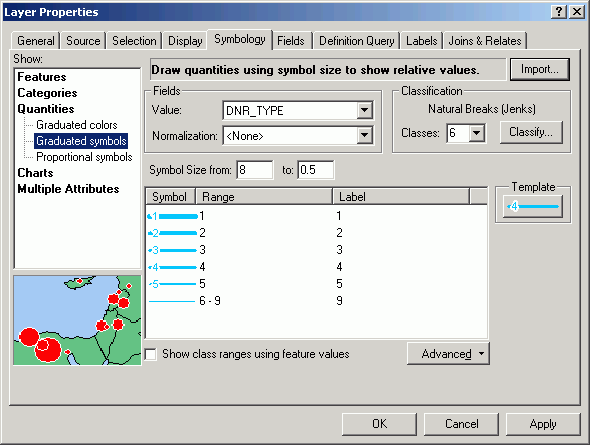
- Add text labels for the roads layer.
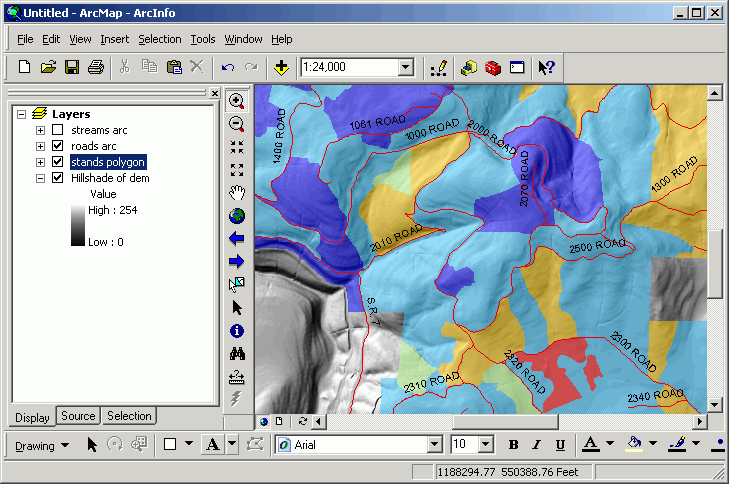
- Create complex symbols for the streams layer, to indicate the DNR stream
type. Start by changing to a graduated thickness symbol with 6 classes.
- Change the label for the 6th symbol to 9 (there are 6 values:
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 9).
- Flip the symbols so the thickest line represents value 1 (DNR type 1
is "most significant").
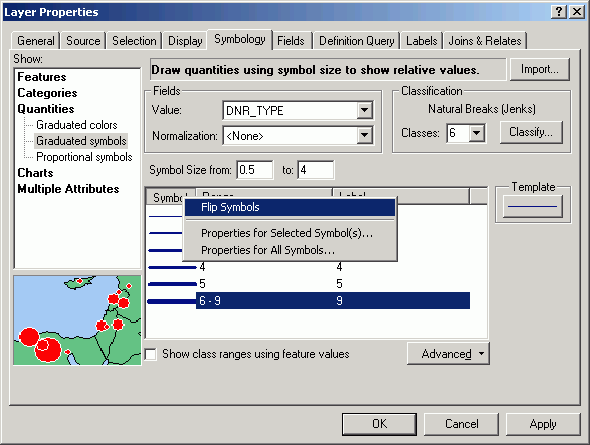
- Change the properties for all symbols (a lighter blue):
- You will be creating a line symbol composed of two layers, one simple line
layer, and another layer with the DNR type number.
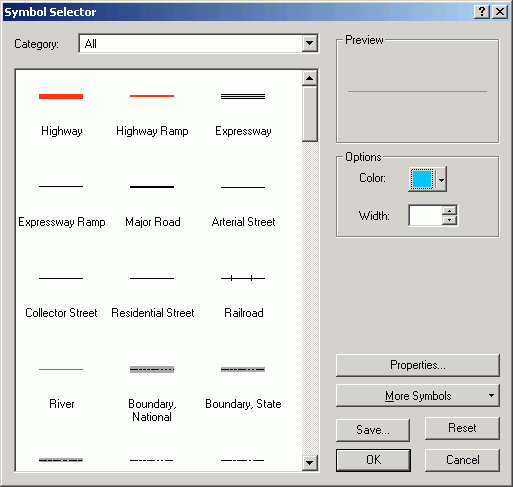
- Open the symbol for class 1. Change its thickness to 4 points.
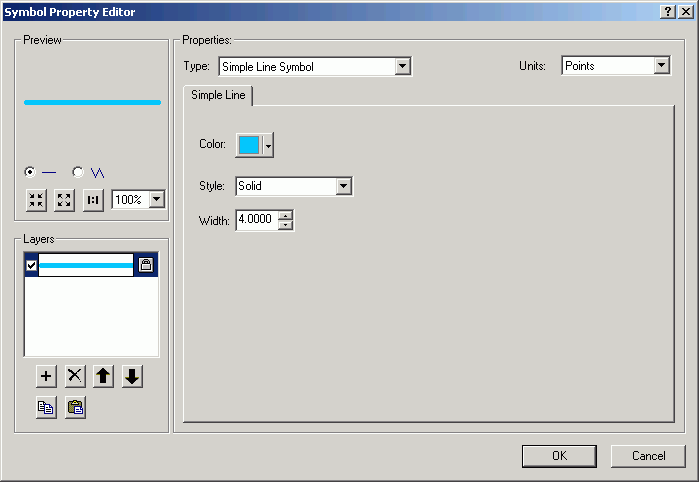
- Click the + button to add another line layer.
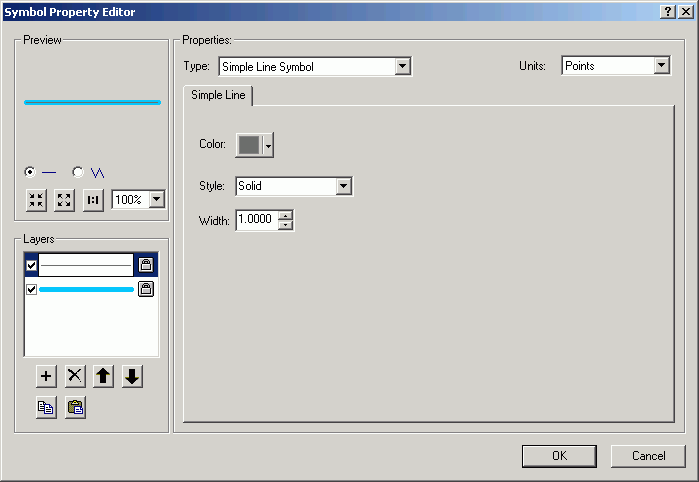
- With the new layer selected, change from Simple Line Symbol to
Marker Line Symbol. Marker lines can be constructed with font symbols.
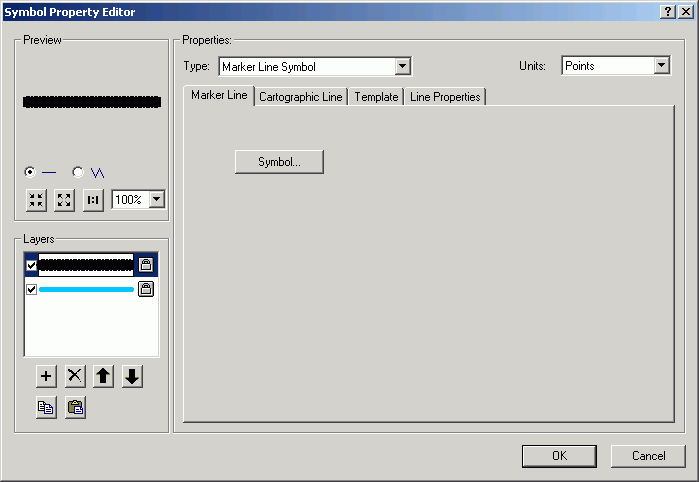
- Click the Symbol.
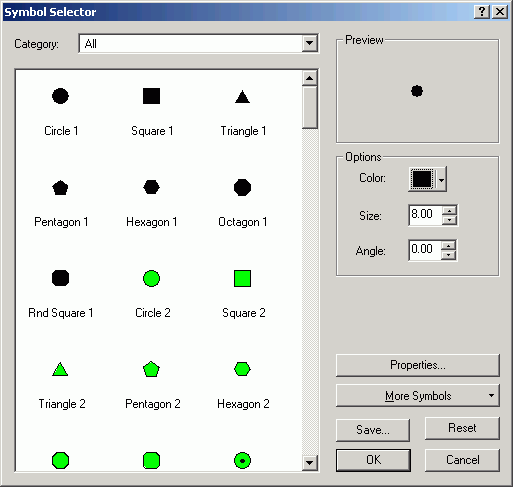
- Click Properties to alter the marker symbol for the marker line.
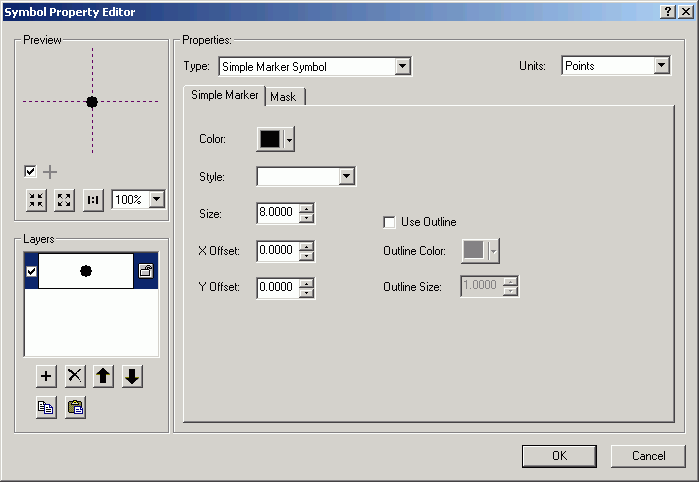
- Change from Simple Marker Symbol to Character Marker Symbol.
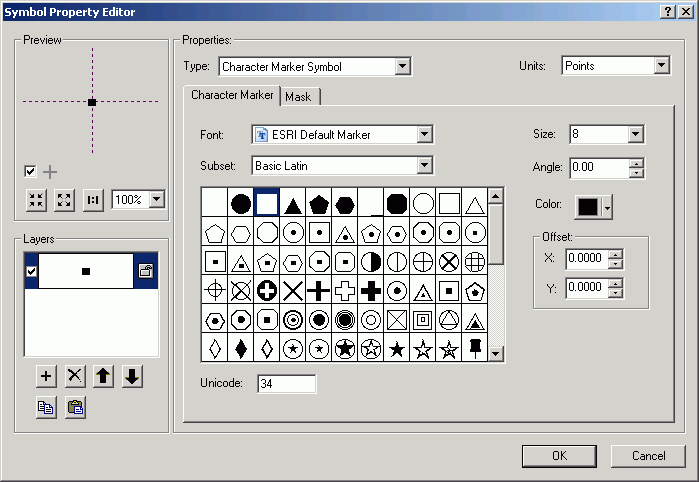
- Change to Arial font.
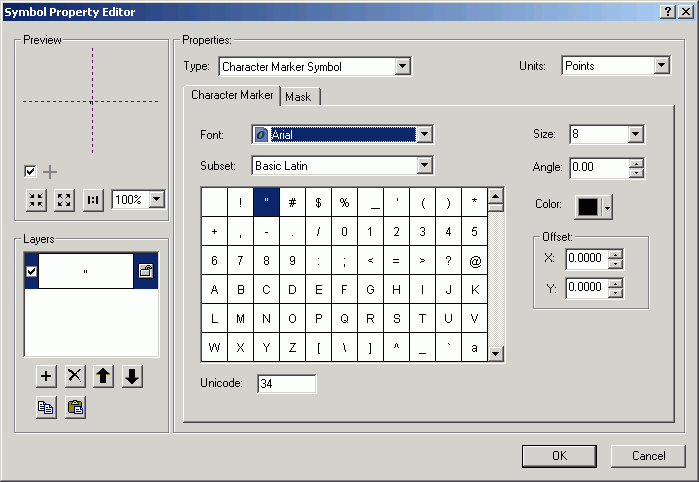
- Select the numeral 1 for the symbol.
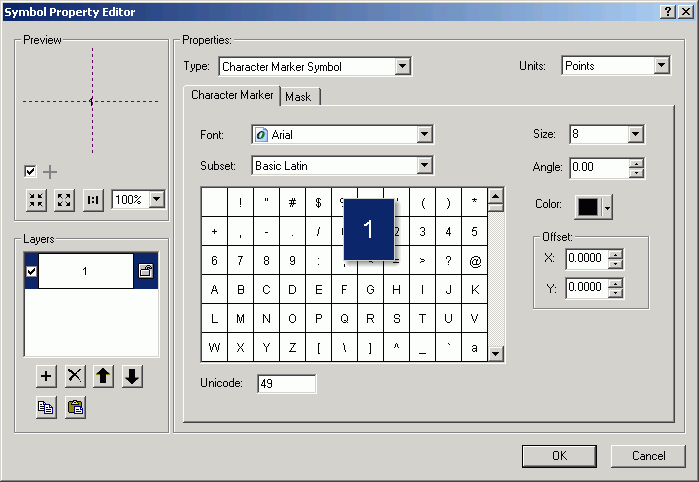
- Click the Mask tab, and specify a Halo of 2 points.
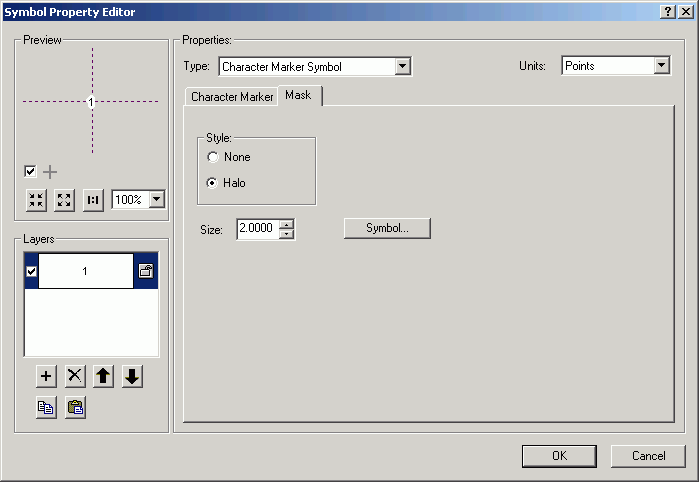
- Alter the color of the symbol to match the line color.
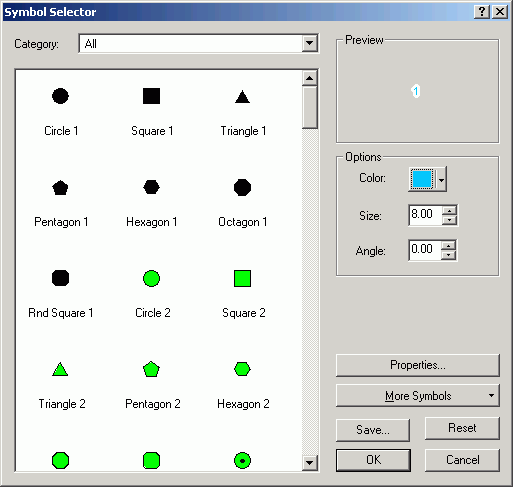
- Click the Template tab to alter the interval.
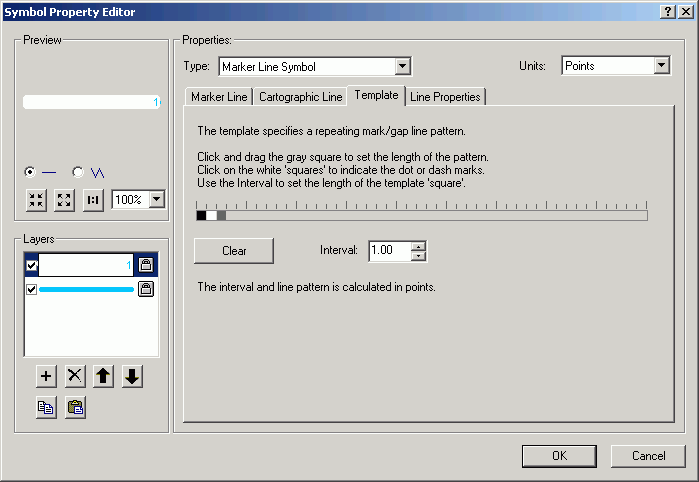
- Change the Interval to 10 points.
Drag the gray square to the 11th position. With an interval of 10 points,
this will separate markers by 100 points (there are 72 points per inch,
so the separation will be about 1.4 in.).
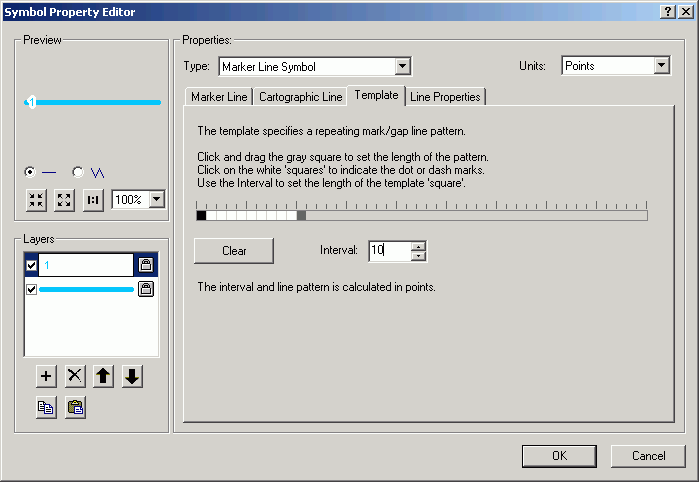
- Now you will see the way the final symbol will appear.
- If you look at the Mashel River at the north of Pack Forest you will
see how the symbol has changed.
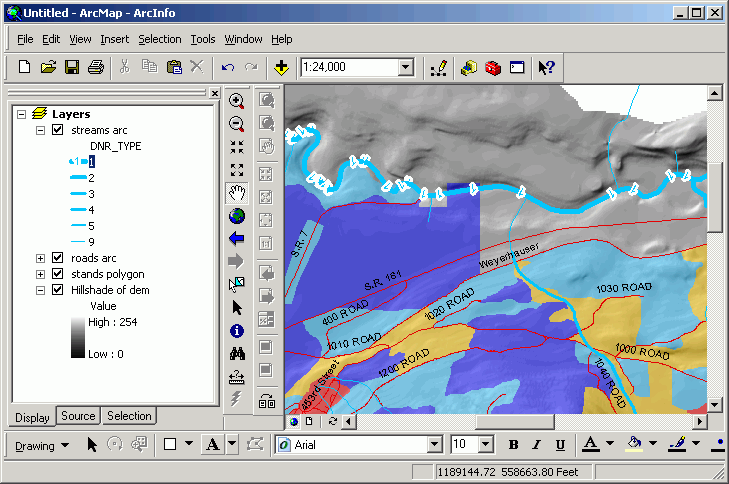
- Alter the other symbols accordingly or download the layer file streams_dnr.lyr
and apply its symbology to your streams. (The layer file was created by
altering all symbols and then right-click > Save as layer file.)
- Open the layer properties for the streams. Click the Import
button. Click the radio button for Import symbology...
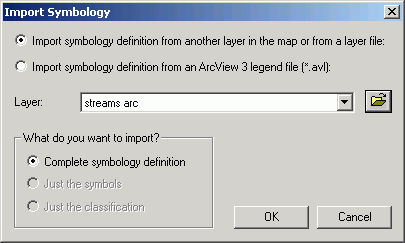
- Select the layer file you downloaded.
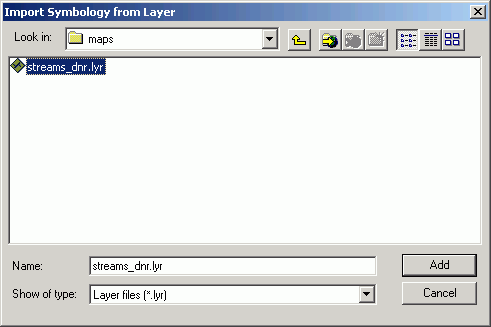
- Match the DNR_TYPE field.
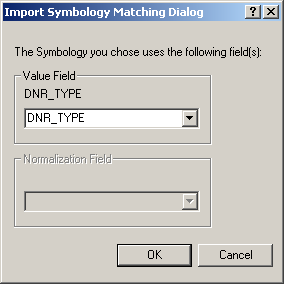
- The layer will now have the same properties as the layer file.
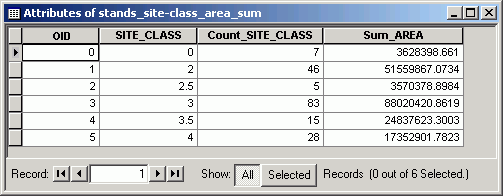
Create a summary table from a attribute table.
- Open the attribute table for stands.
- Create a summary table for the SITE_CLASS with the summary statistic
ACRES > Sum.
Create a graph
- Create a graph from the summary table.
- Alter the graph elements and properties so that the graph is formatted the
way you want it. Refer to the lesson
on tables if you need to review graph making.
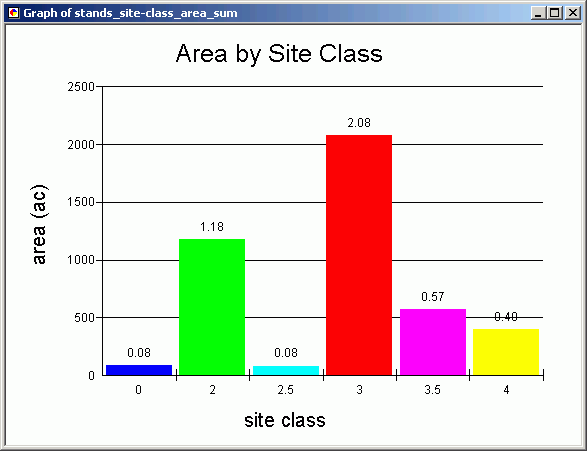
- Change the colors of the data markers to match the symbology for the stands.
To do this, right-click on the graph and select Advanced Properties > Data. Click the icon showing a matrix of colors at the lower right of the Editing dialog. Double-click on a data marker and then select its color.



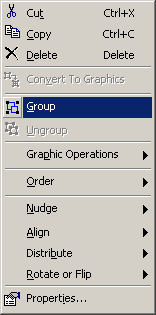
Create a layout and alter properties.
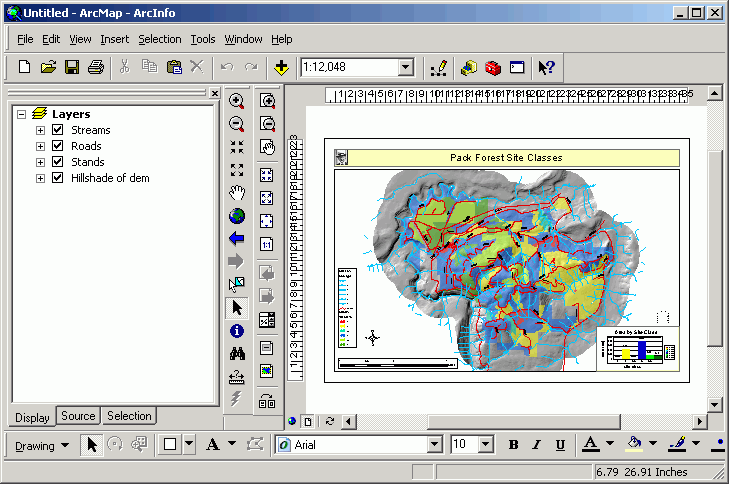
Layouts are an integral part of ArcMap. In order to see layout view, click
the Layout view icon  below the lower left of the map display.
below the lower left of the map display.
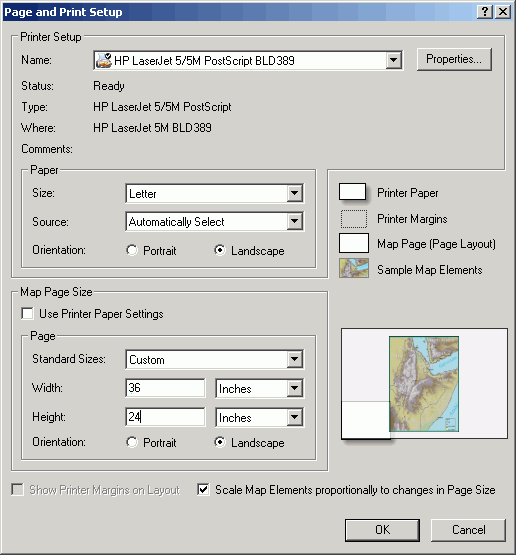
- Change the page properties by selecting File > Page and Print Setup.
- Set the orientation to Landscape.
- Uncheck Use Printer Paper Settings.
- Alter the size for a poster sized layout (Width = 36 in; Height = 24 in).
- Click Scale Map Elements....
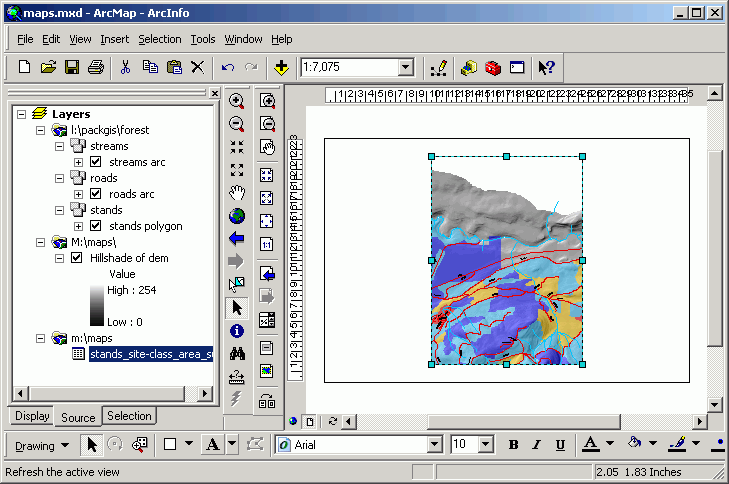
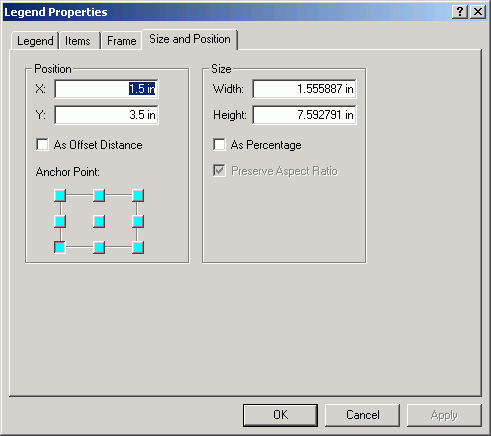
- Right-click on the data frame and select Properties.
- Set the Anchor Point at (1, 1).
- Change the Size to 34 x 20.
Note: while it is possible to change the size and position of map
elements manually with the selection handles and the pointer tool,
if you set size and positions of elements using coordinate values,
it is much easier to get elements to line up.
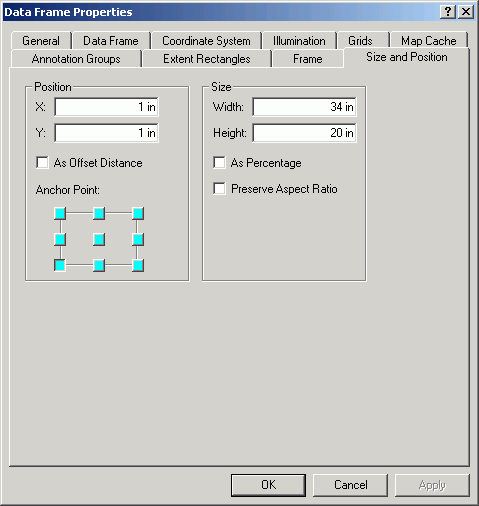
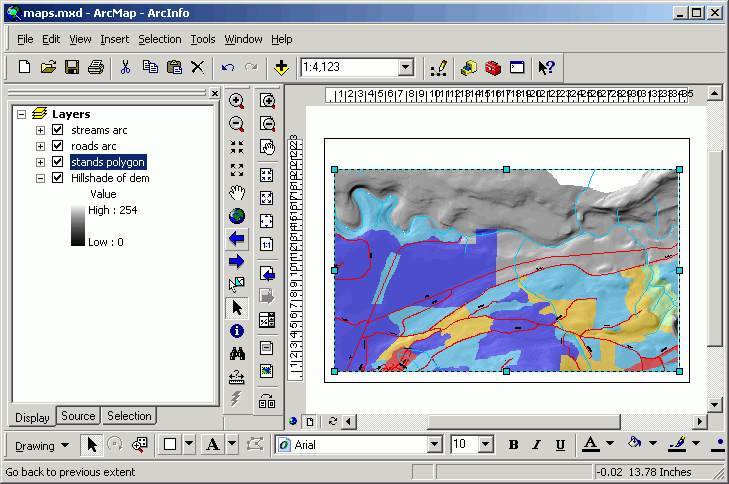
- Work with the zoom and pan tools until the map is in the position you
like.
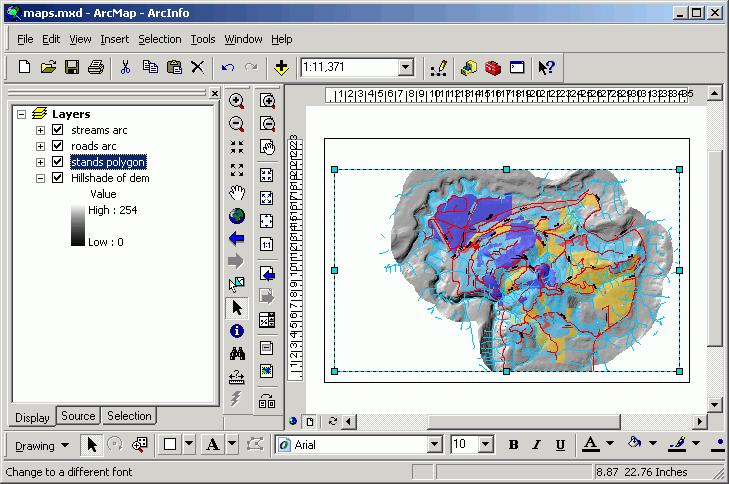
Add elements to the layout
- Graph
- If you have closed the graph, open it again (Tools > Graphs).
- Right-click the title bar of the graph and select Show on Layout.
- Close the graph again.
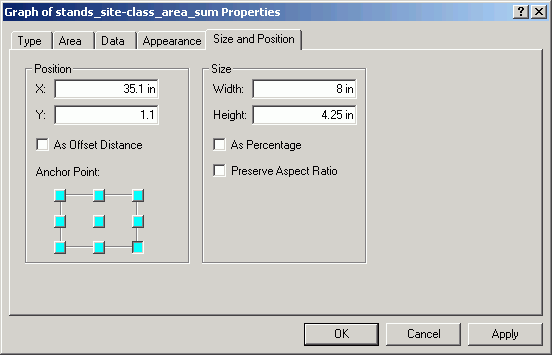
- Position the graph on the layout as below (right-click > Properties).
This will offset the graph by 0.1 in from the map border. Note how the
Anchor Point is used to position the graph.
.
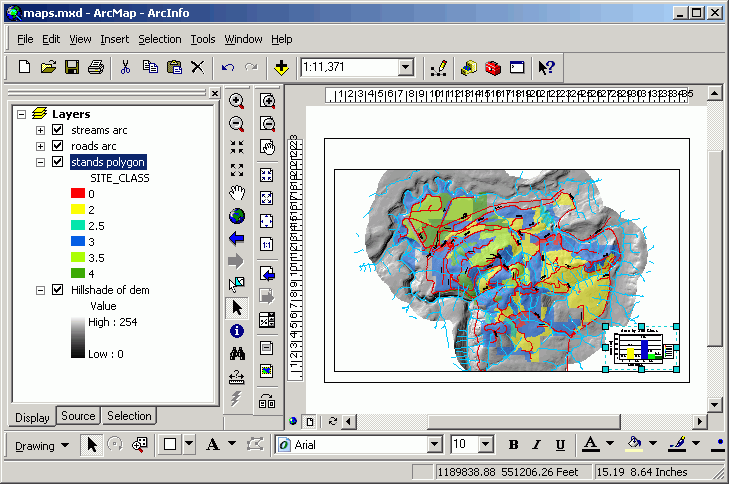
- Add a rectangle (on Drawing toolbar). Alter its properties to line up
with the map border. Note how the Anchor Point is used to position
the rectangle.
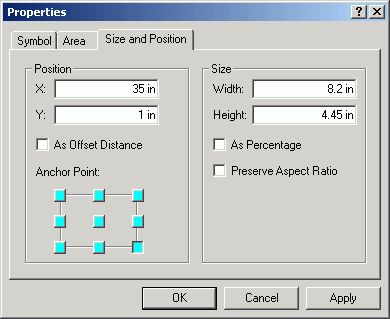
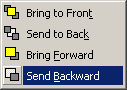
- Send it behind the graph (right-click > Send Backward)
- Select both the graph and the rectangle by using the pointer (not
the drawing tool) to drag a rectangle that contains both objects. Group
them by right-click > Group). Now if you were to reposition
or resize the graph, it would always have its border.
- Title Text
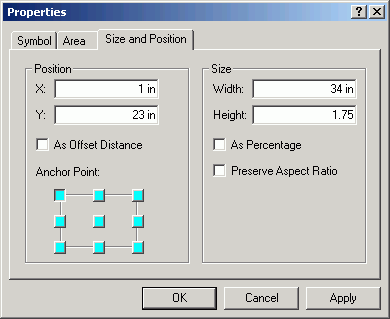
- Add a rectangle at the top of the map. It will be used to hold the title
text. Alter its properties as below. This will give a 0.25 in gap between
the text box and the map border.
- Add a text element (also on the Drawing toolbar) for the title.
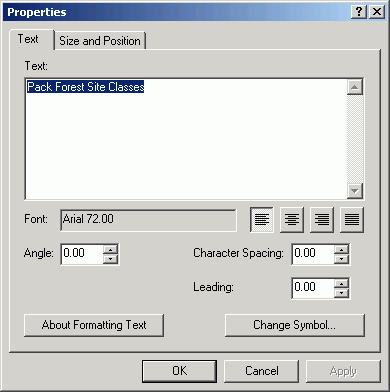
- Change Symbol and specify a font size of 72 points (1
in).
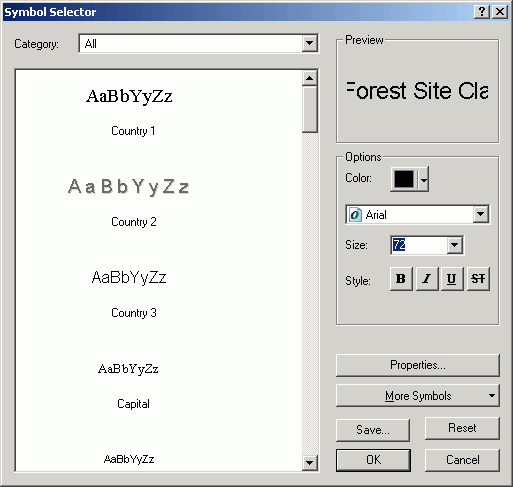
- Change the position so it is about in the middle of the rectangle.
- Select both the rectangle and the text and right-click > Group.
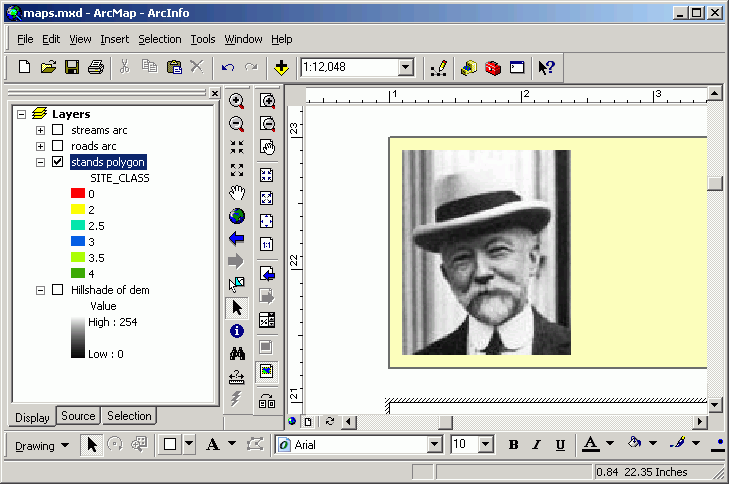
- Graphic
- Save to a local drive either the CFR logo
 , the Forest
Engineering logo
, the Forest
Engineering logo  , or Charles Pack's photo
, or Charles Pack's photo  .
To save, right-click on the image and use the menu choice to save the
image as a file in M:\maps.
.
To save, right-click on the image and use the menu choice to save the
image as a file in M:\maps.
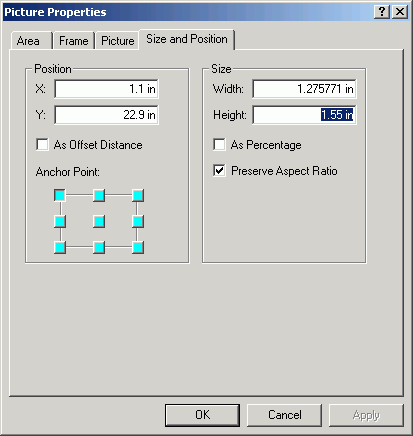
- Select Insert > Picture. Navigate to M:\maps and you
will see a list of graphics files.
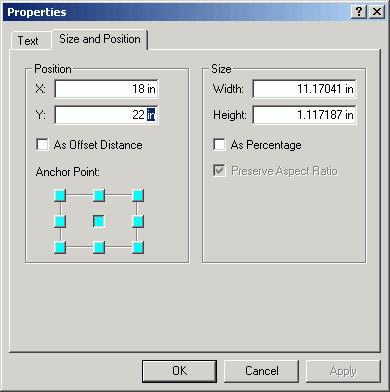
- Alter the position to place the image in the title box. Note that Preserving
Aspect Ratio will keep the image with the same proportions. The Height
is selected to be offset from the title box by 0.1 in on the top and bottom.
The Position sets its location also as the offset.
- Zoom in with the Layout Zoom In tool
 to make sure the position is correct.
to make sure the position is correct.
- Zoom back out to full view
 .
Note that some of the layers can be turned off in order to speed up drawing.
.
Note that some of the layers can be turned off in order to speed up drawing.
- Scale bar
- Add a scale bar (Insert > Scale Bar). Select the Alternating
Scale Bar 1 and then click Properties.
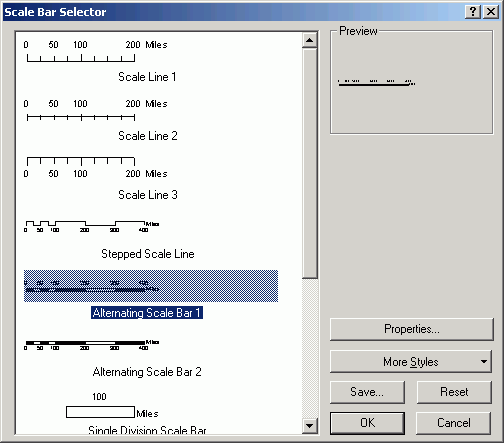
- Alter the properties:
- Set Division Units to Miles.
- Set When resizing to Adjust number of divisions.
- Change Division value to 1.
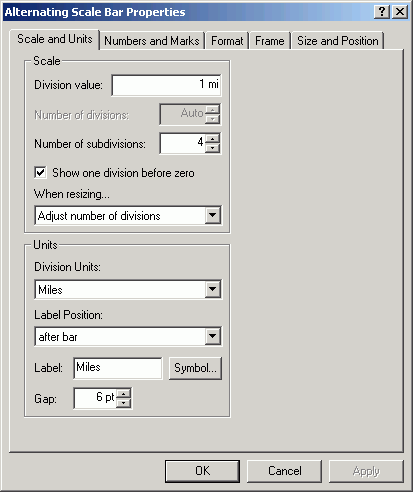
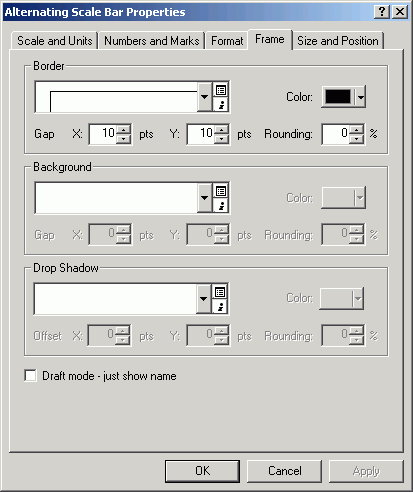
- Add a frame border. Increase the Gap to 10 points
on each side of the scale bar.
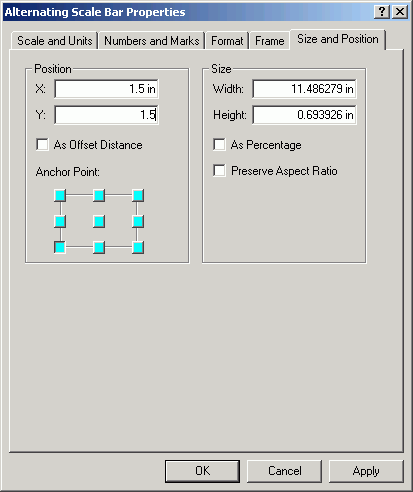
- Set the Position to be 1.5 in in each direction from the
corner of the map sheet.
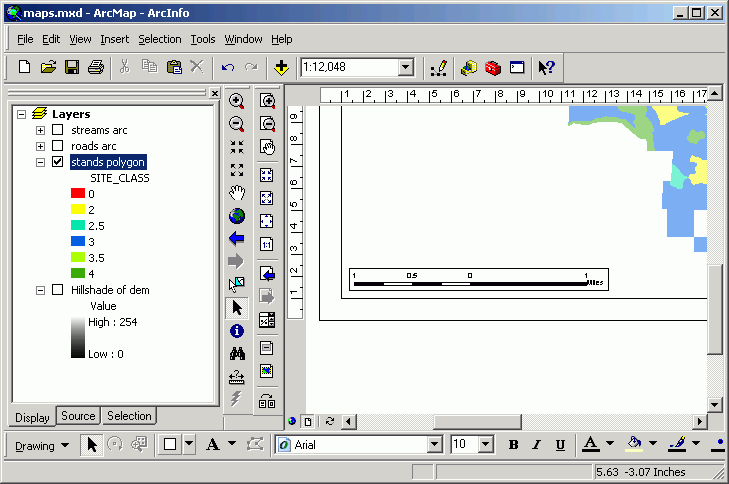
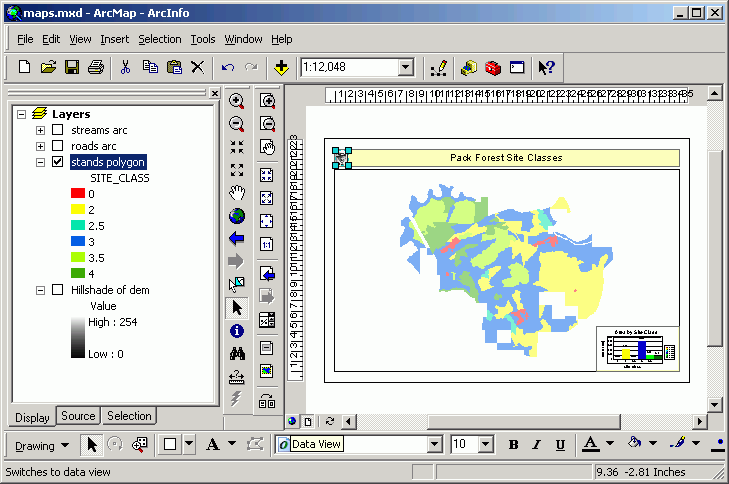
- Legend
- Add a legend by using the Insert > Legend menu choice.
Select the layers to include by clicking the Add button  .
.
You can also remove layers by clicking the Remove button  .
.
Order in the legend can be altered by using the Up  or Down
or Down  tools.
tools.
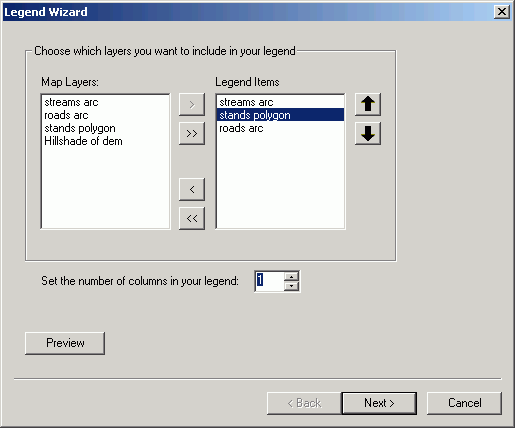
- Click Preview to have the legend added to the layout. Keep clicking
Next until you see the Finish button, then click Finish.
- Note the names of the layers appear on the legend exactly as shown in
the Table of Contents. If you alter the Table of Contents and the layer
properties the changes will automatically be updated in the legend.
Change the names of the layers to make them more readable:
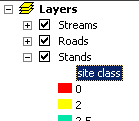
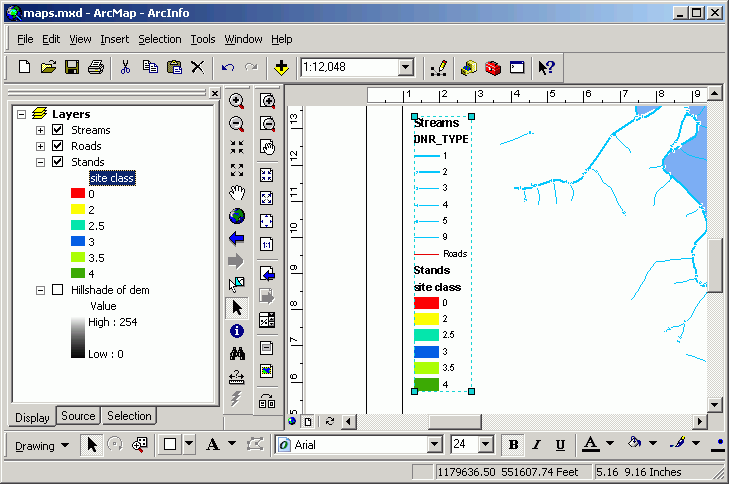
Now you see the legend already looks better:
- Right-click the legend and select Properties.
Uncheck Show for the legend title (it should be obvious this is
a legend).
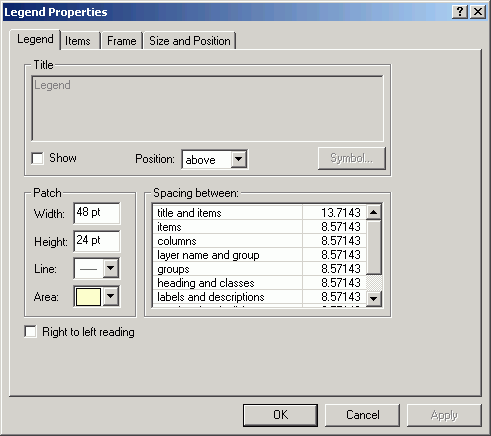
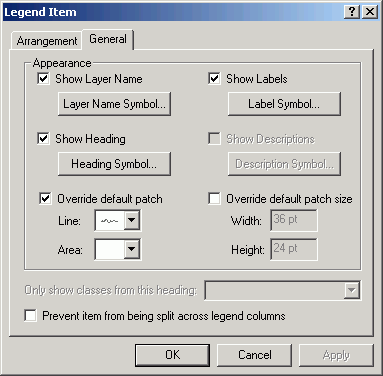
- Click the Items tab. Select stands and click Style.
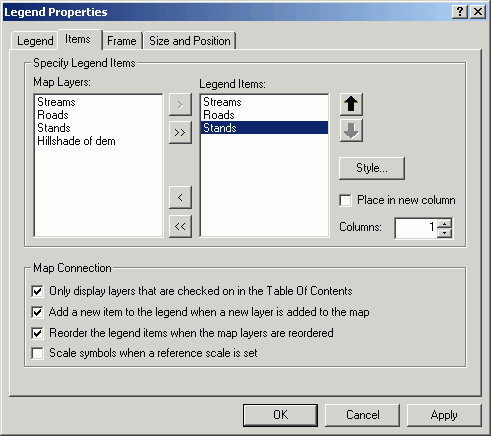
- Click Properties.
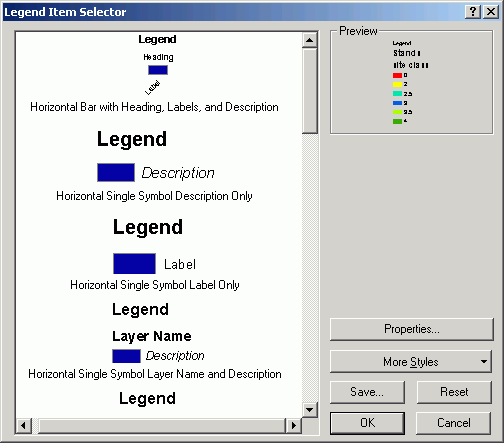
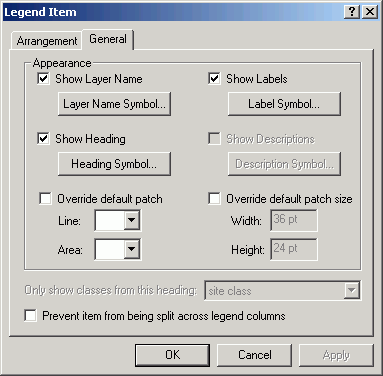
- Click the dropdown for Area to select a symbol to override the
default rectangle legend patch.
- Select Natural Area. This has a shape more like a forest stand
polygon.
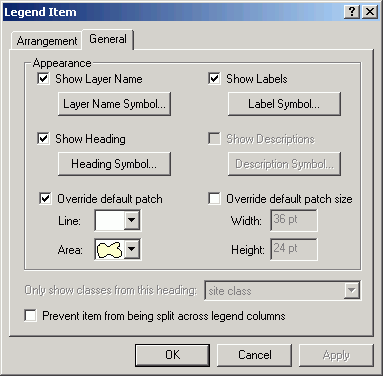

- Click OK until you return to the Items tab. Change the
Style for Streams.
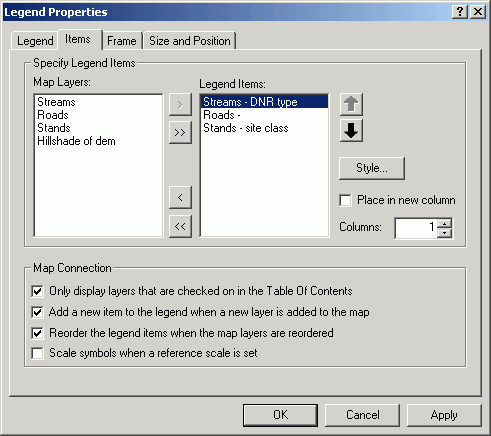
- Alter its Line symbol as Flowing Water.

- Alter the Roads symbol to a ZigZag.
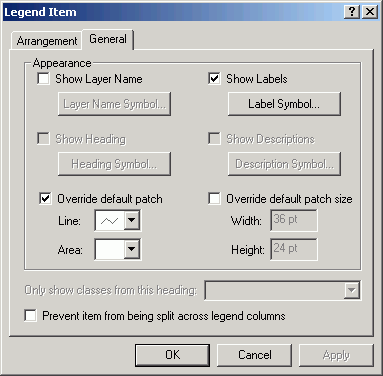
- Change the position of the legend.
- Zoom to print size
 to inspect the legend as it will appear after being printed.
to inspect the legend as it will appear after being printed.
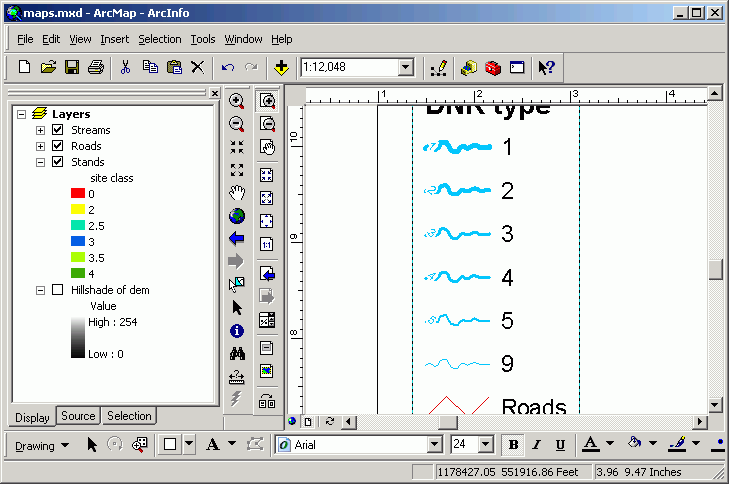
- North Arrow
- Now add a north arrow to the layout. Select Insert > North Arrow.
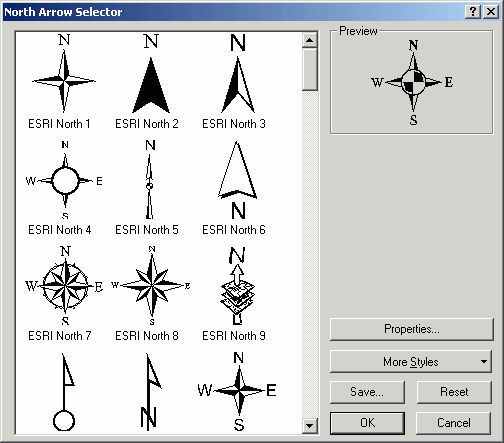
- Select the style you want and click OK. [NOTE: simpler is better, that way attention will be drawn to the more important map features.]
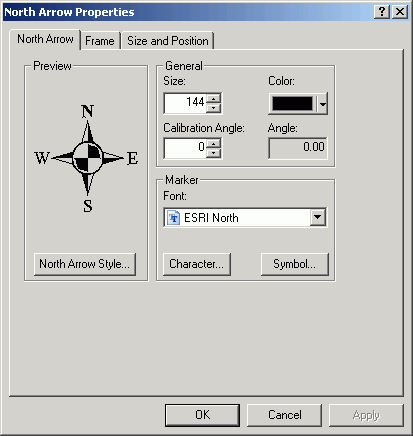
- Right-click the north arrow and select Properties.
- Alter the size to 144 (2 in)
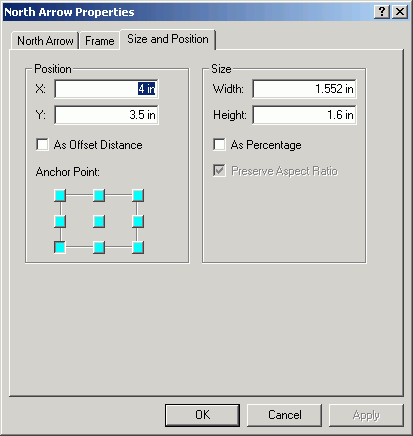
- Change the position.
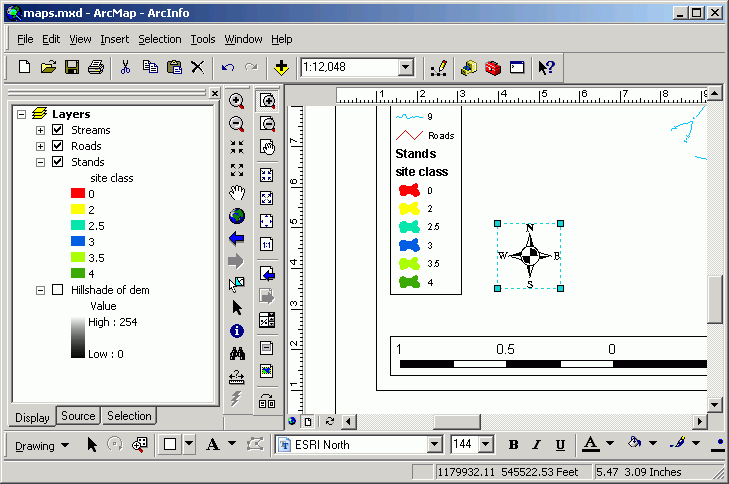
- Table
- Click the Source tab in the Table of Contents.
- Double-click the summary table to open its properties.
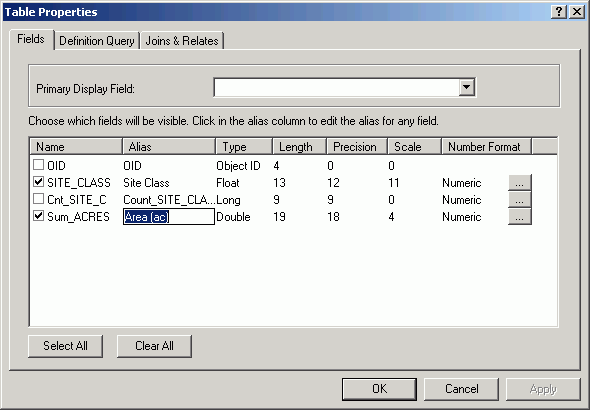
- Uncheck the fields OID and Cnt_SITE_CLASS. Change the
aliases for the fields SITE_CLASS and Sum_ACRES as below.
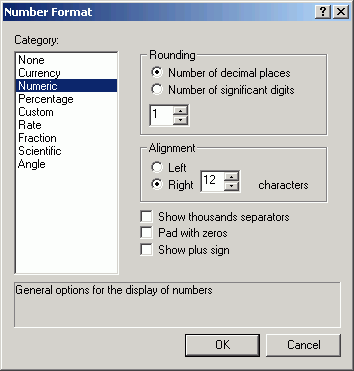
- Click the ellipsis for Number Format for the Sum_ACRES
field. Change the Number of decimal places to 1.
- Click OK and then open the table.
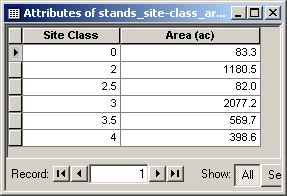
- Click Options > Add Table to Layout.
- Reposition the table as you like.
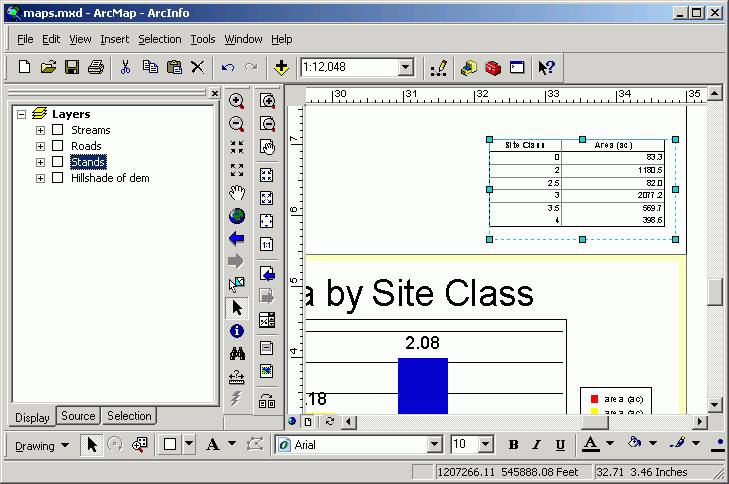
- Save the map document now.

Save the layout as a template
If you need to make a series of maps that have the same overall design, you
can save the map as a template.
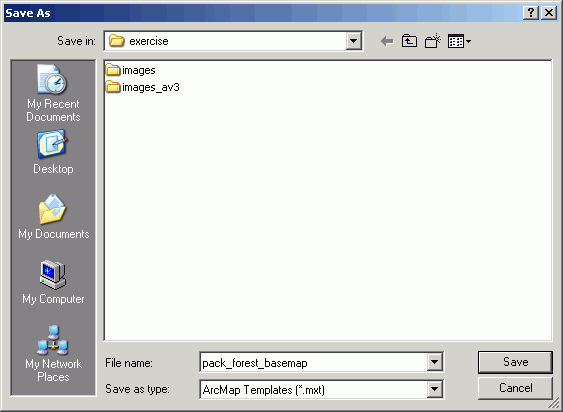
- From the File menu, select Save As. Alter the file type to
ArcMap Template and the name to pack_forest_basemap.
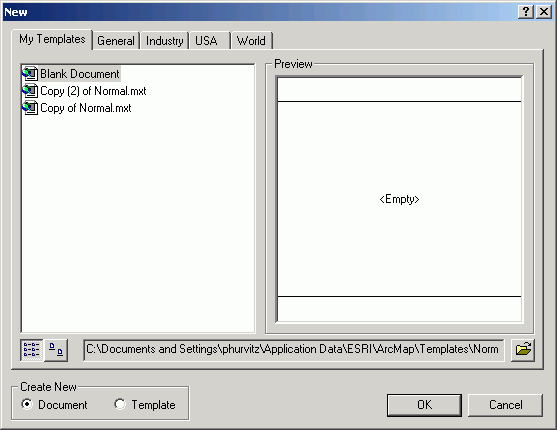
- From the File menu, select New. This gives you an opportunity
to select a template. Click the Browse button.
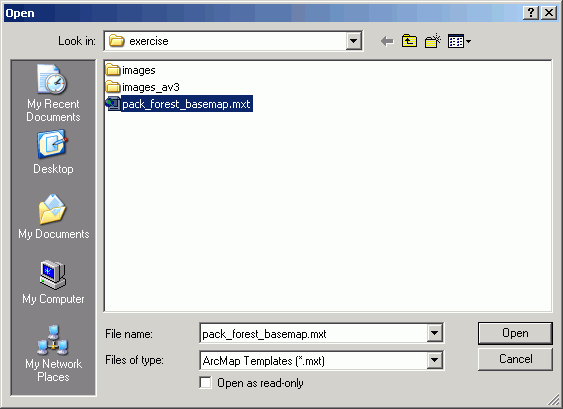
- Select the template you just created
- Note the new map will look exactly like the previous map document, but it
will be called Untitled. You can make alterations to this map document
and then save the changes to an mxd file.
Why use a template when you could simply open an existing map document and
Save as to another map document? There is a possibility if you open an
existing map document and make changes that you could inadvertently overwrite
the original copy. In addition, you can store map templates in the general template
location, which is more convenient than searching for a map document that may
be several branches deep in the file system.
Print the layout
You will not actually be printing the layout, but this step will create a PDF
file that you could print later if you wish.
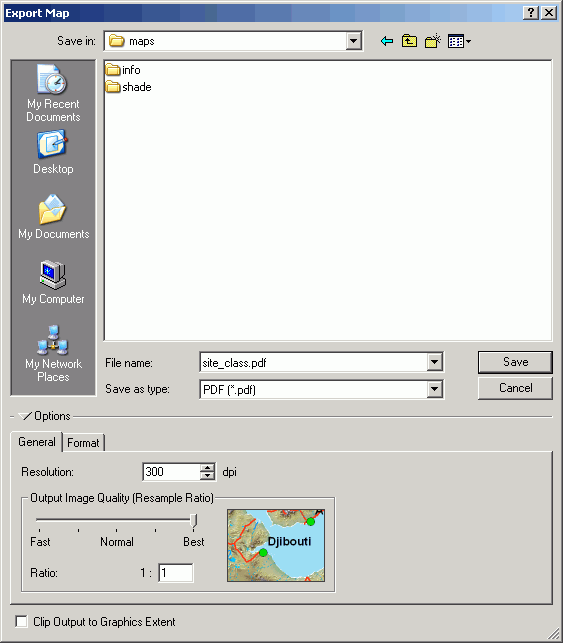
- From the File menu, select Export Map.
- Navigate to M:\maps. Select the file type PDF with a resolution
of 300 dots per inch. Most large-format printers cannot print higher
than 300 dpi.
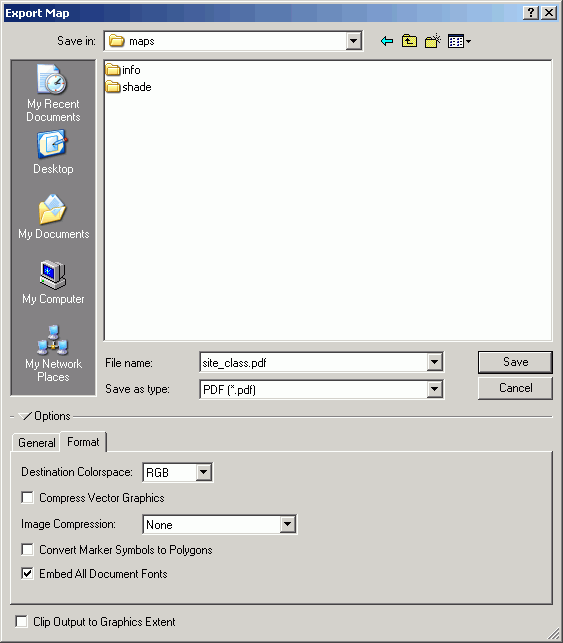
- Alter the Format to disable compression for Vector and Image data
(to give the best quality) and to Embed All Document Fonts. When fonts
are embedded, the document should be able to open properly on computers that
do not have any of the special ESRI fonts (e.g., north arrow) installed.
- Click Save. It may take some time for the PDF to be rendered if you
are not on a fast machine.
- After the PDF is created, open it in Adobe Arcobat.
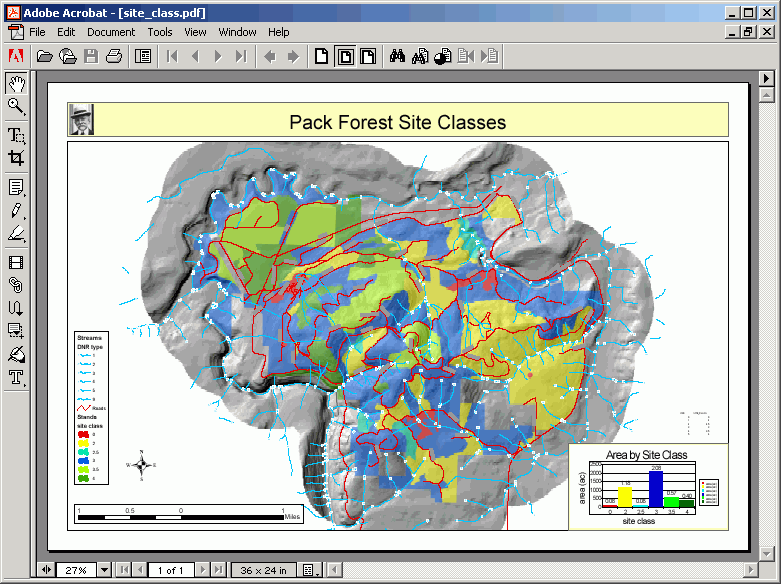
- You can print to a letter-sized page from Acrobat if you want a hard copy.
Get more practice
- If you are inclined, you can get more practice with map layouts by altering
the current layout or creating a new one.
- Experiment with creating more layouts, using data in the L:\esridata
directory.
- Create several maps of the same basic data, but with a few different audiences
in mind, or with different objectives for communication.
REMEMBER TO TAKE YOUR CD AND REMOVABLE DRIVE
WITH YOU!!!!
Return to top
 |
|
TThe University of Washington Spatial Technology, GIS, and Remote Sensing
Page is supported by the School of Forest Resources
|
|
School of Forest Resources
|


































![]() below the lower left of the map display.
below the lower left of the map display.














 , the Forest
Engineering logo
, the Forest
Engineering logo  , or Charles Pack's photo
, or Charles Pack's photo  .
To save, right-click on the image and use the menu choice to save the
image as a file in M:\maps.
.
To save, right-click on the image and use the menu choice to save the
image as a file in M:\maps.







































