Introduction to Geographic Information Systems in Forest Resources
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems in Forest Resources |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Drive Substitution
Perform drive substitution to create the virtual drives L and M.
Conceptual Understanding:
Why is this necessary?
How can you get different computers to use the same drive
letters?
Getting ArcMap to "connect" to different drives
What if drive letters L and M are in use, or if network drives are using drive letters I want to
use?
Operational instructions
Practically, how can we switch the CD drive (virtual drive) into L drive and the Removable drive into M drive for following lab exercises have been covered in the following steps.
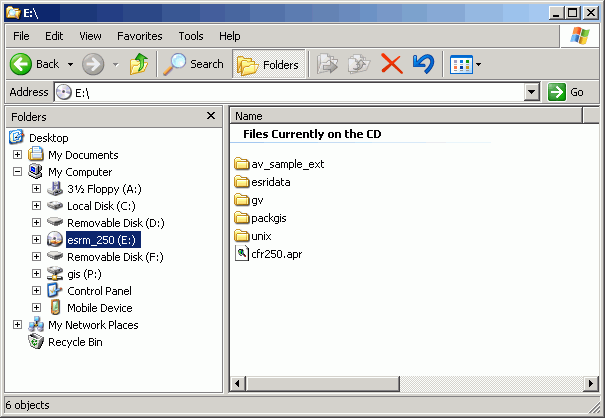
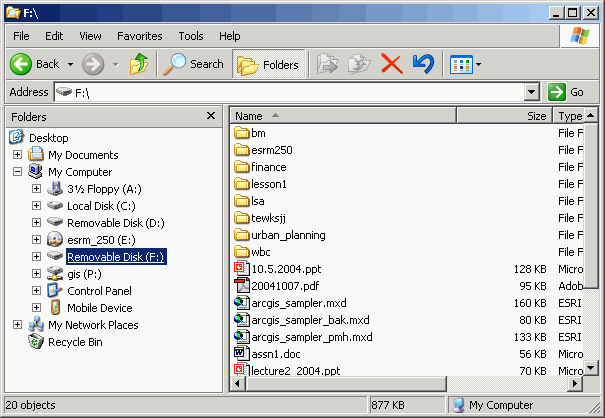
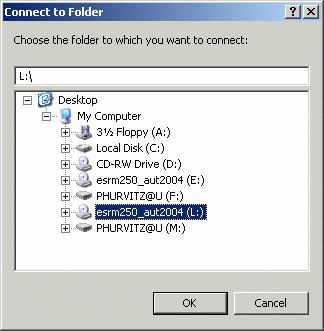
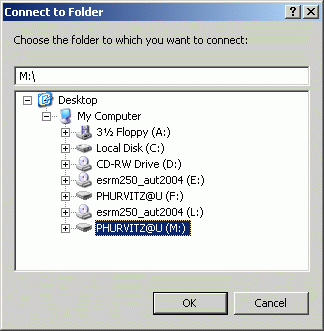
When you move to a different computer, repeat steps (2 & 3) before starting ArcMap. Your map documents will always open without orphan datasets (unless, of course, you have left data on the hard drive of the other computer).
If you have made an incorrect drive mapping, you will need to delete the drive substitution before you can use the drive letter again. The best way is re-login to your computer.
There is a possible way you can re-map with the correct drive letters by typing differemt command from the CMD windown. For example, to remove a substitution on drive L from D drive:
subst l: /d
Why is this necessary?
Map documents do not contain data, but merely contain instructions for loading and displaying data. Suppose you create a map document in which the data were loaded from your course CD, on a computer on which the CD drive letter is D. Now, if you move to a different machine where the CD drive letter is E, the map document will not "know" where the data are (it will look for drive D but not find the data it expects to be there). Likewise, suppose you have saved data on your removable drive on drive letter F, but the other computer assigns your removable drive to letter G. If this is the case, when you move to a different machine and open your map document, your map document will not find the data sources and will have layers that are "orphaned."
Here is a map document with two layers.
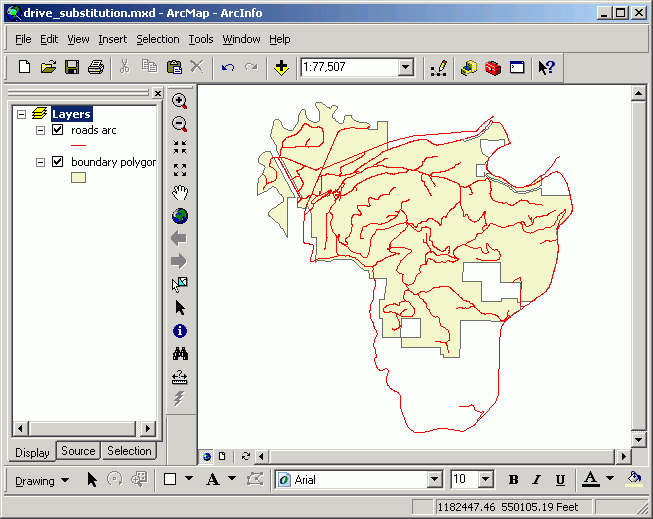
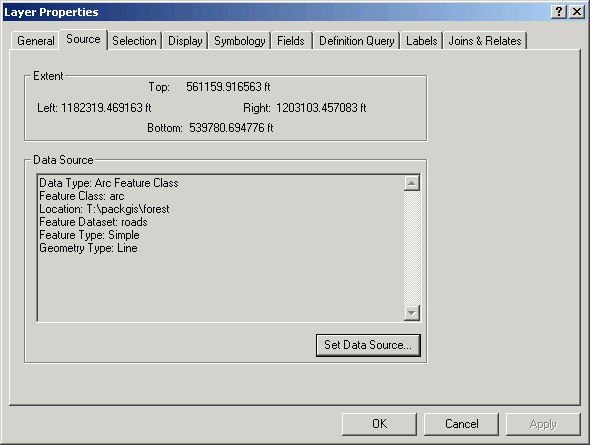
Note from layer properties (right-click on the layer in the table or contents and select Properties) the data source for the roads layer is on drive letter T (see Location: T:\packgis\forest). Drive letter T happens to be a CD drive on one of my computers.
Now, suppose I save the map document and move to a different computer, where the CD drive is letter J. When I open the map document, the layers will not display, because there is no location T:\packgis\forest on this computer. The red exclamation points indicate the layers cannot be displayed because their data sources are not found.
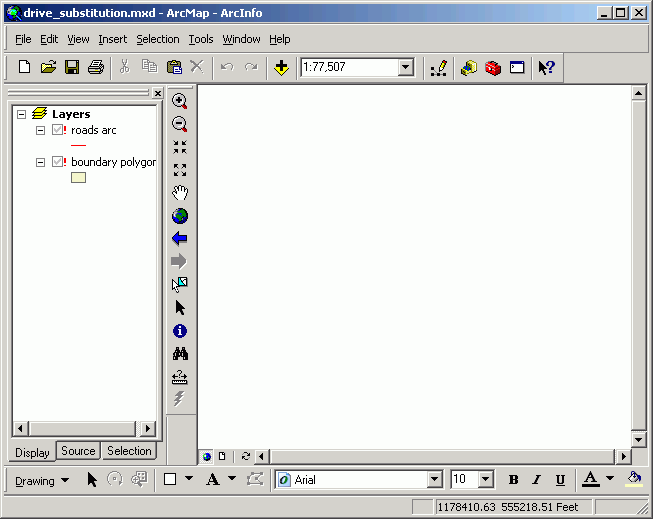
But this situation, which you will probably run into during this quarter many times as you move from machine to machine, can easily be solved, as described below.
How can you get different computers to use the same drive letters?
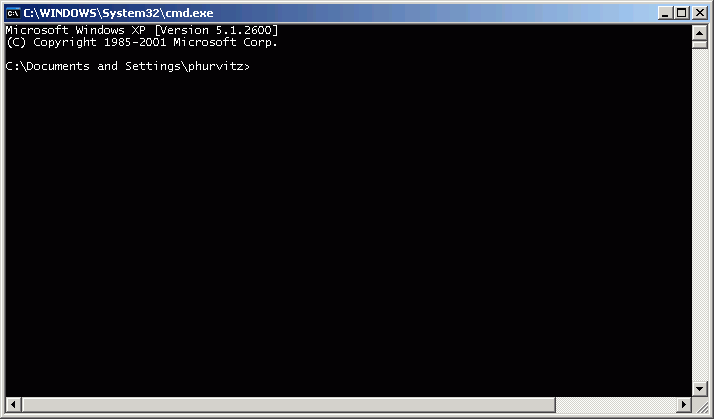
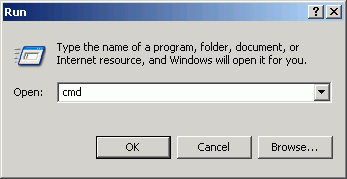
There is a little-known, but very old trick in the Microsoft operating system for "drive substitution," which creates virtual drive letters. Given the previous situation, suppose you are on a computer that has no drive T (where ArcMap expects to find your data) but does have a drive J, where the CD is loaded. You need to get the computer to recognize drive T as the CD drive. To do this, open a command prompt (easiest way is to click the Start button and select Run, then enter the string cmd, which opens a command window.

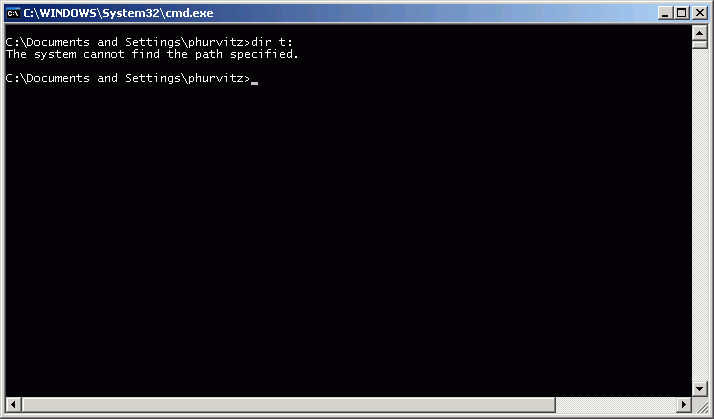
If you try to get a directory listing of the contents of drive T, you will get an error, because drive T does not exist.
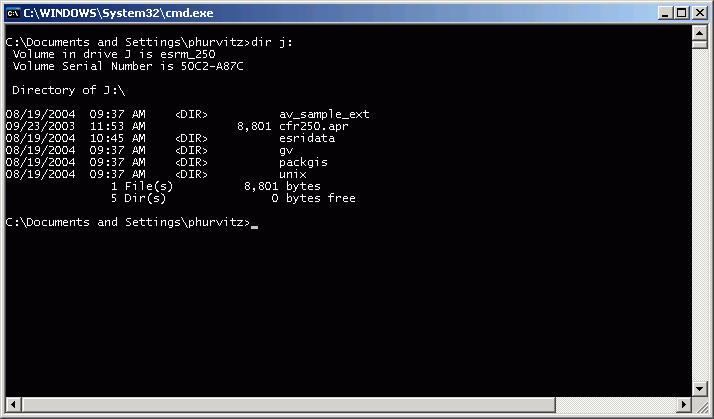
However, drive J does exist, and has the contents of the CD:
What we want to do is get the contents of drive J (the CD) to show up under drive T (the CD drive letter from your other computer).
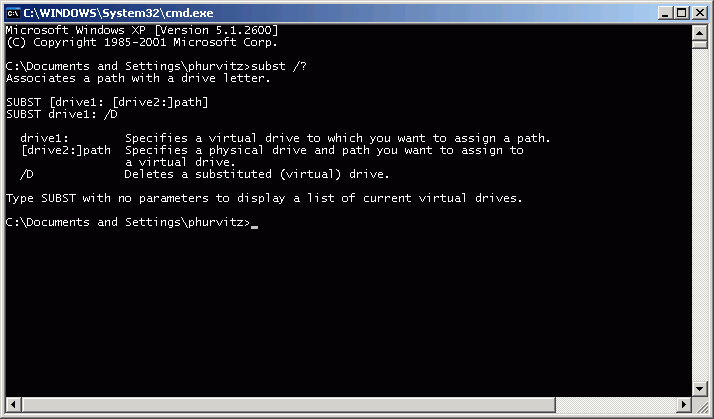
In the command window, type subst /? to get usage for the subst command:
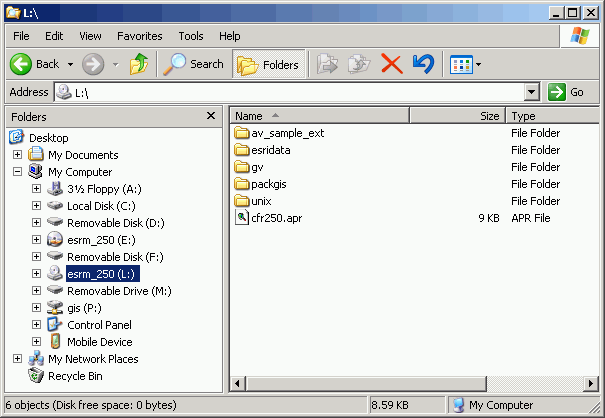
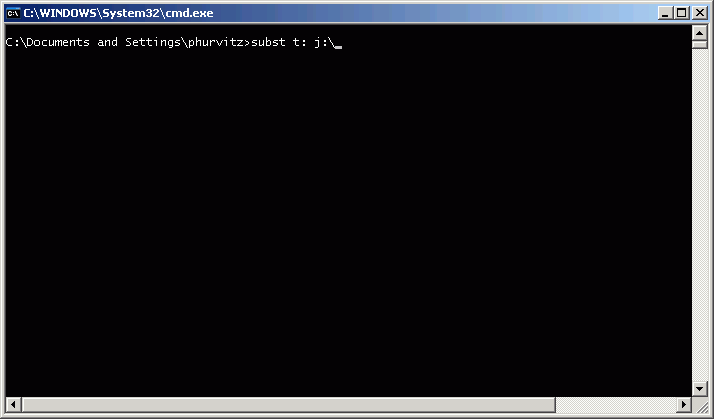
Following the previous example, to create a "virtual" drive T from the CD drive (J:), enter the string subst t: j:\, as shown below:
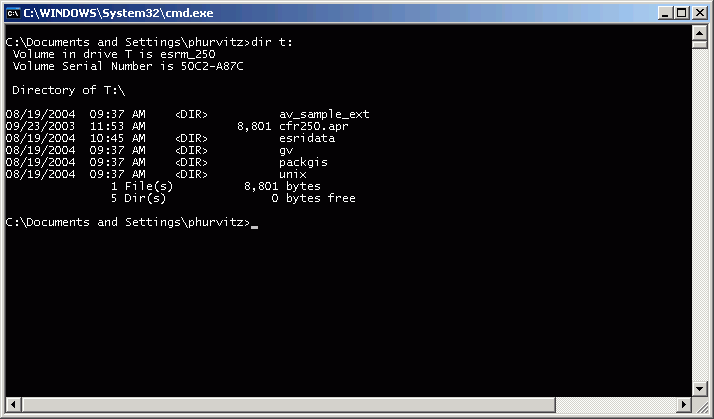
Now drive T will have the same contents as drive J, and ArcMap will have no problem finding data where it expects.
Getting ArcMap to "connect" to different drives
Once you have the computer recognizing your
virtual drive, you may still need to get ArcMap to connect to the new drive. To
do this, open ArcCatalog and click the Connect to Folder button ![]() . This will open a dialog that will allow you to connect to
folders and drives that are not seen by default. Following our previous
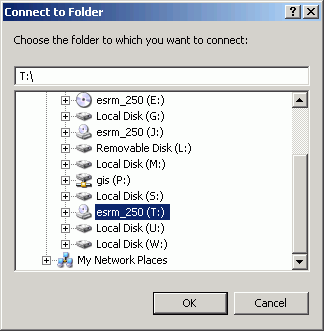
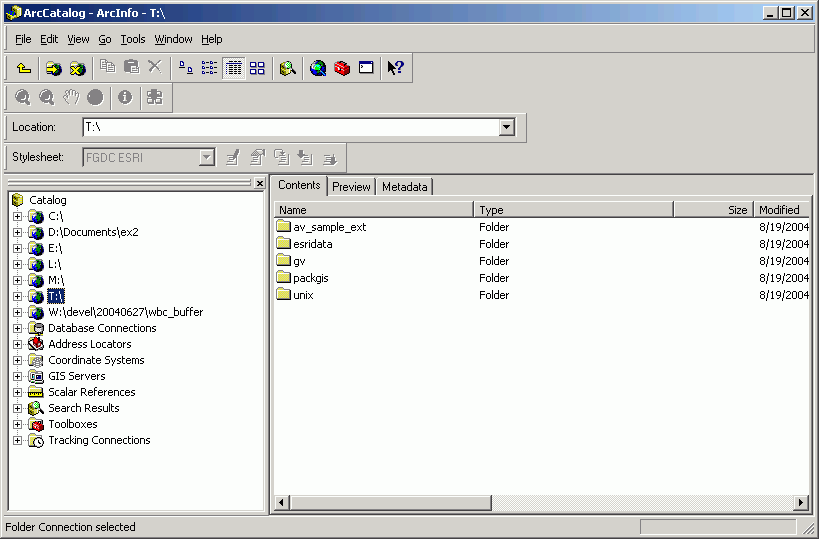
example, select drive T as the folder to connect to, and click OK.
. This will open a dialog that will allow you to connect to
folders and drives that are not seen by default. Following our previous
example, select drive T as the folder to connect to, and click OK.
Now drive T will show up in ArcCatalog, and you can use it as though it were a regular drive letter, although no "real" drive T exists on this machine!
Note you will need to perform this process each time you move to a different machine, and you will need to substitute and connect to both the CD and your removable drive. Also, you will want to perform this process before you do any work to create a map document.
What if my computer already has drives with letters L and M?
To get the map documents in the course to load data properly, it is necessary that your computer has drive letters L and M mapped to the CD and removable drives, respectively.
You must either change your drive letters to something else so you can subst L and M for the course data, or in the map documents, set data source to the drive letters representing the CD and removable drives.
What if network drives are using drive letters I want to use?
Especially on computers that are in labs, there may be connections to networked drives. Usually these connections can be broken without ill effect.
Suppose you have created a map document on a computer where you have substituted drive J for the CD and drive P for the removable drive. But you move to another computer on which drive P already appears to exist. You can break the connection with drive P by going into the Windows Explorer and disconnecting the networked drive.
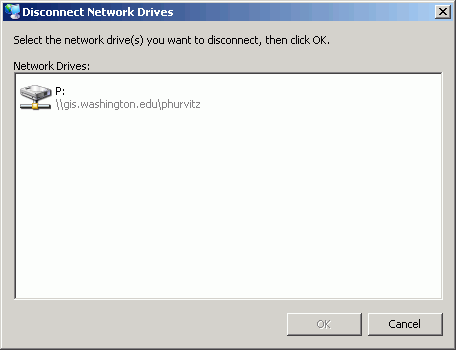
From the Tools menu, select Disconnect Network Drive.
This opens a dialog displaying the networked drives. Select the drive(s) you want to disconnect and click OK. This will free up the drive letter P and then you can go ahead and substitute your current removable drive with drive letter P.
|
|||||||||||||||
|
The University of Washington Spatial Technology, GIS, and Remote Sensing Page is supported by the College of Forest Resources |
College of Forest Resources |